CS224W-Machine Learning with Graph-Link Prediction and Causality
The 3 rungs of the ladder of causation
Rung 1: Associational
- Traditional graph machine learning tasks
- Assume
- Task: Predict output form input
- Data: samples of
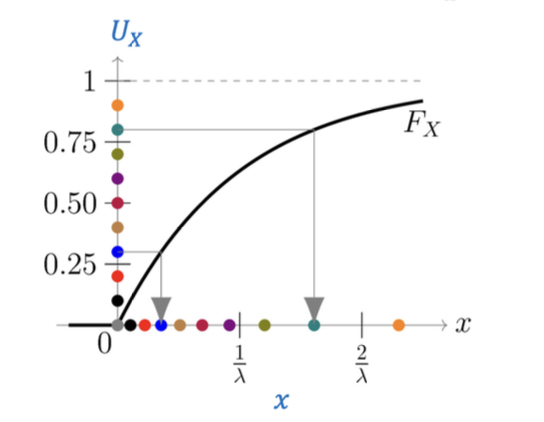
Background: Inverse Transform Sampling
- Data generation algorithm:
- Let be a random uniform value in the interval
- Then,
- Exponential distribution example: with inverse
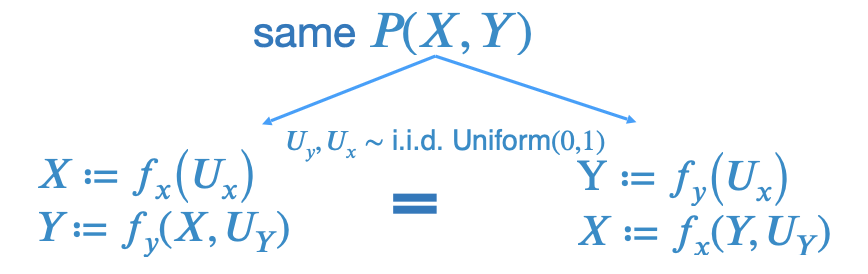
Rung 2: Interventional (cont)
Imagine two hypothetical data generators for
do changes to a constant in data generation
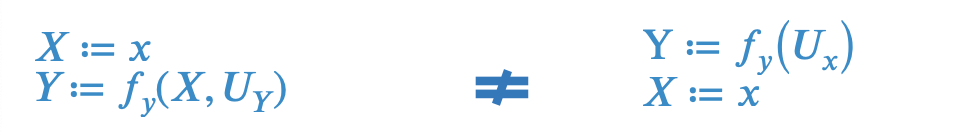
Rung 3: Counterfactual
Imagine two hypothetical data generators for
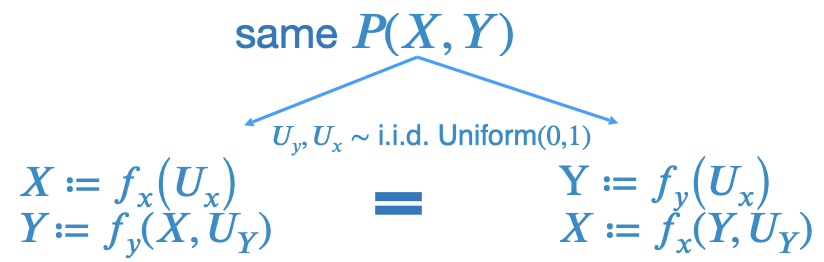
Now assume we know , . This knowledge changes distribution of and
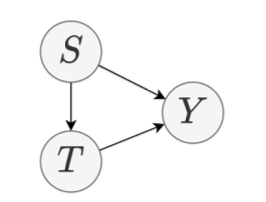
Casual DAG
- Representing causal dependencies using graphs (example in the extra notes)
-
-
-
where are independent variables.
The above data generation can be described by an execution graph, called the causal Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG):
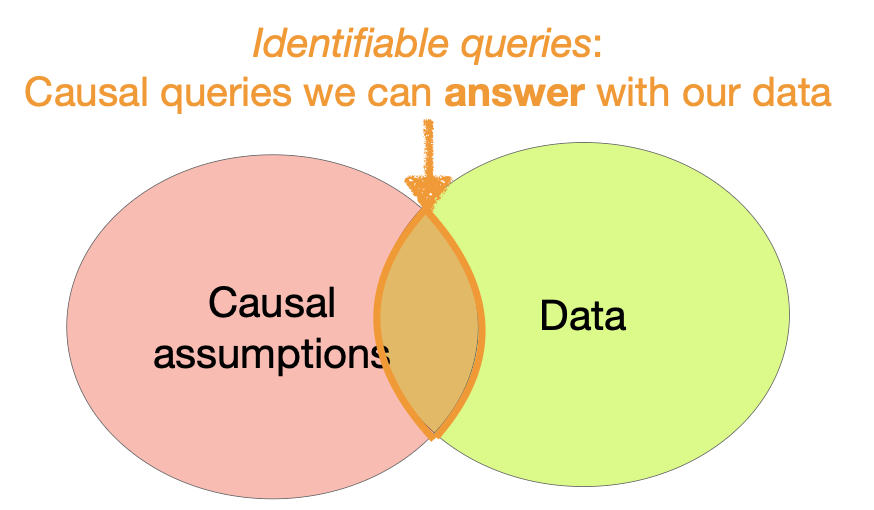
Causality Challenge: Identifiability
Link prediction for decision-making interventions (e.g., search & recommendations) tends to be causal
Importance of Causality in Decision-making
Zillow House Offer Example
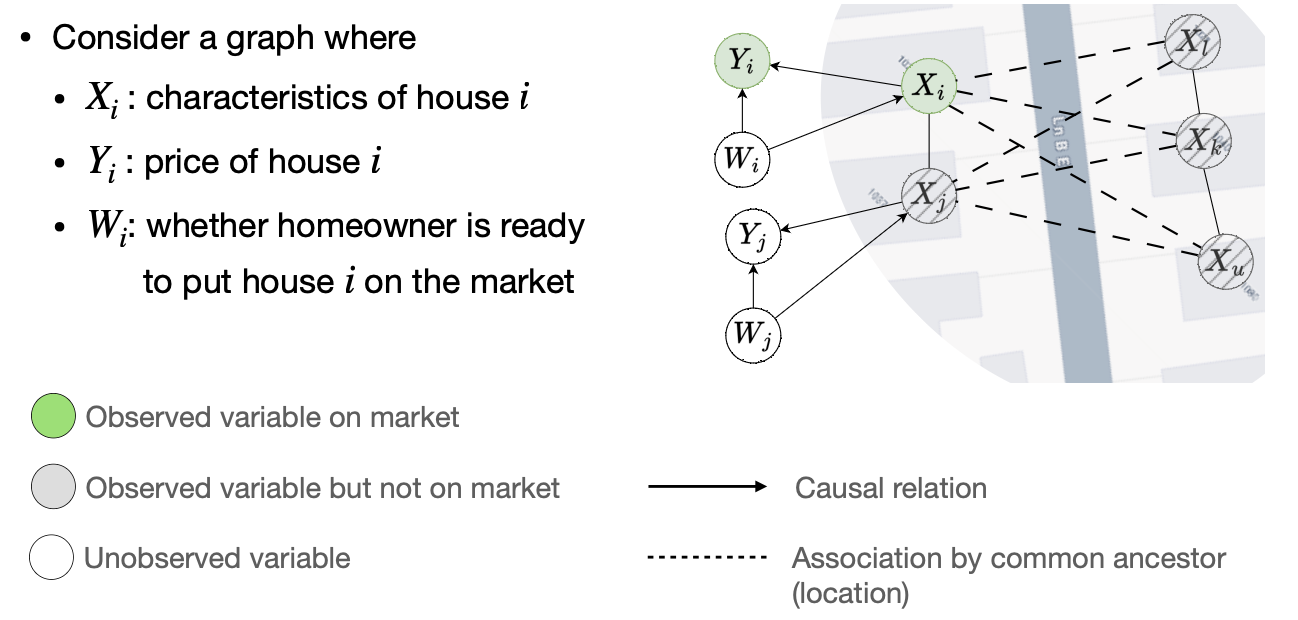
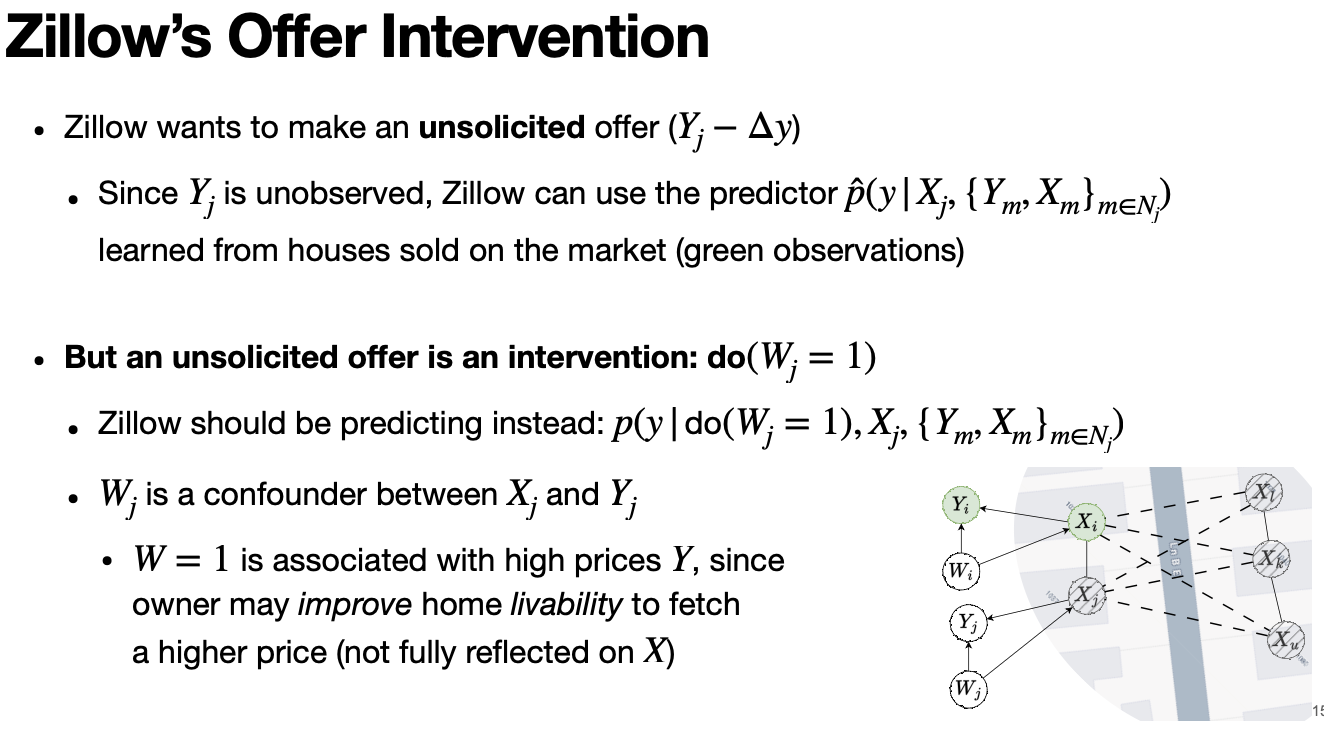
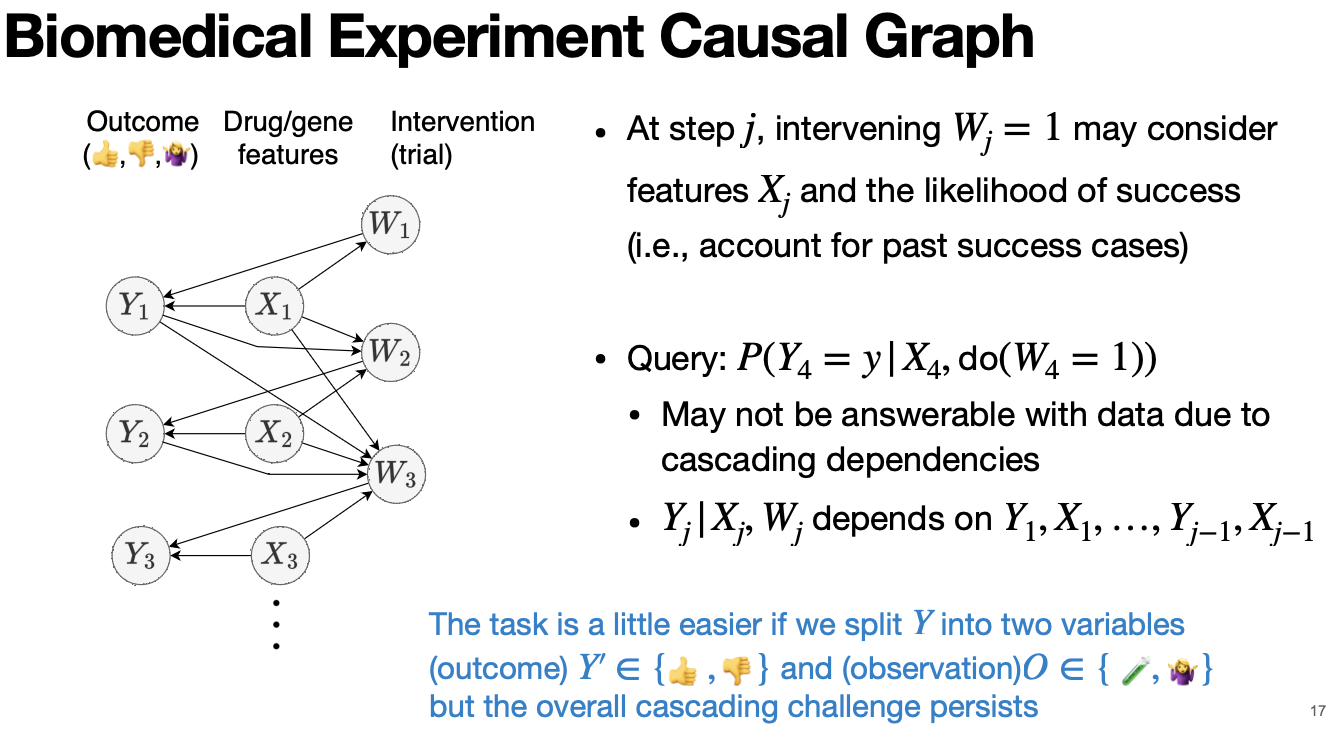
Biomedical Experiment Causal Graph
Other Applications of Causality in Graph Learning
(Out-of-distribution Graph Tasks)
Consider an out-of-distribution graph classification task
- Training data:
- Test data: Predict given ,under and
- where
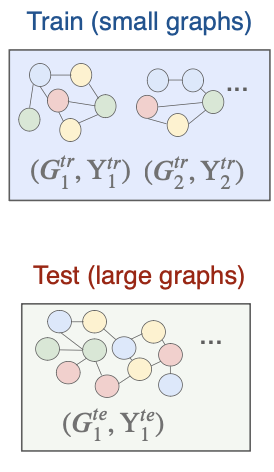
Differences between In-distribution and Out-of-distribution tasks
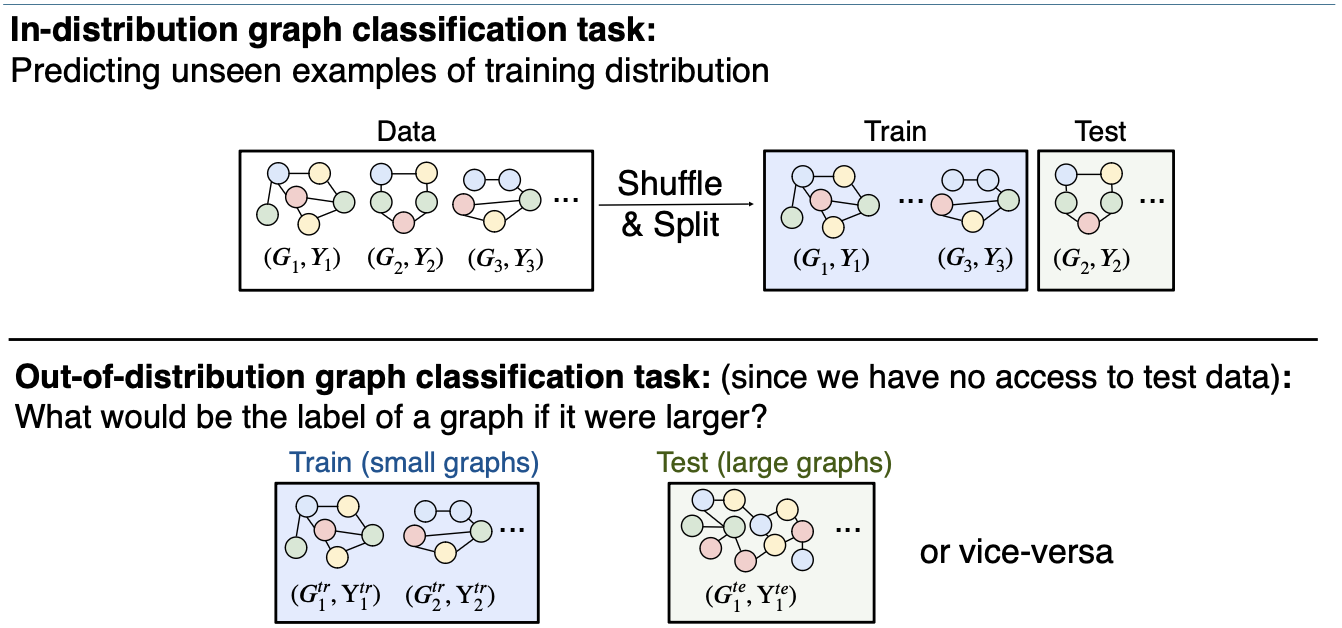
Out-of-distribution tasks are a mix of associational and counterfactual tasks
- Out-of-distribution tasks are associational
Data:
Task: Predict given under
- But the learning is counterfactual
- Without examples from graphs in test
- The classifier must build a correct predictor for unseen graph sizes
Why is Graph ODD Learning a Counterfactual Task?
Example:
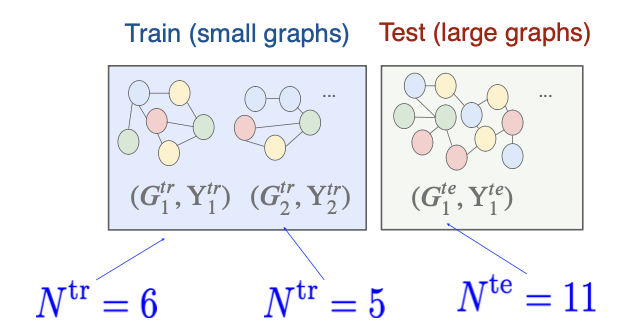

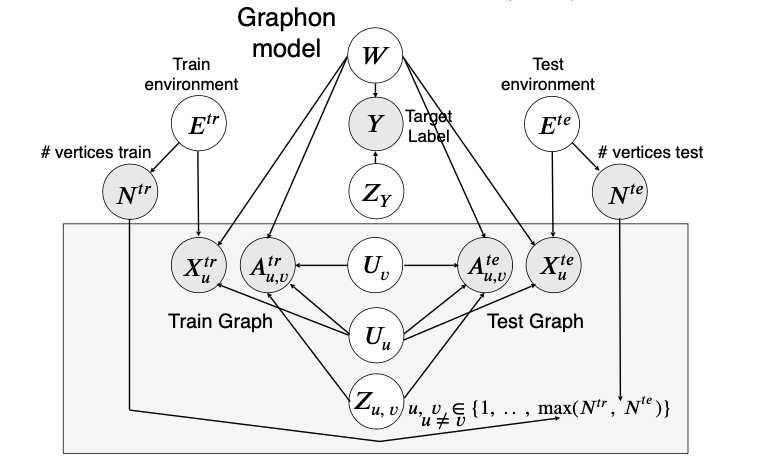
A Causal Mechanism for Graph Sizes
- Graph fromation process (Graphon):
- Graph label is a function of the graph model & some random noise
- Graph size is a function of “environment” only
- Train (test) graphs are generated by and with same random noises.
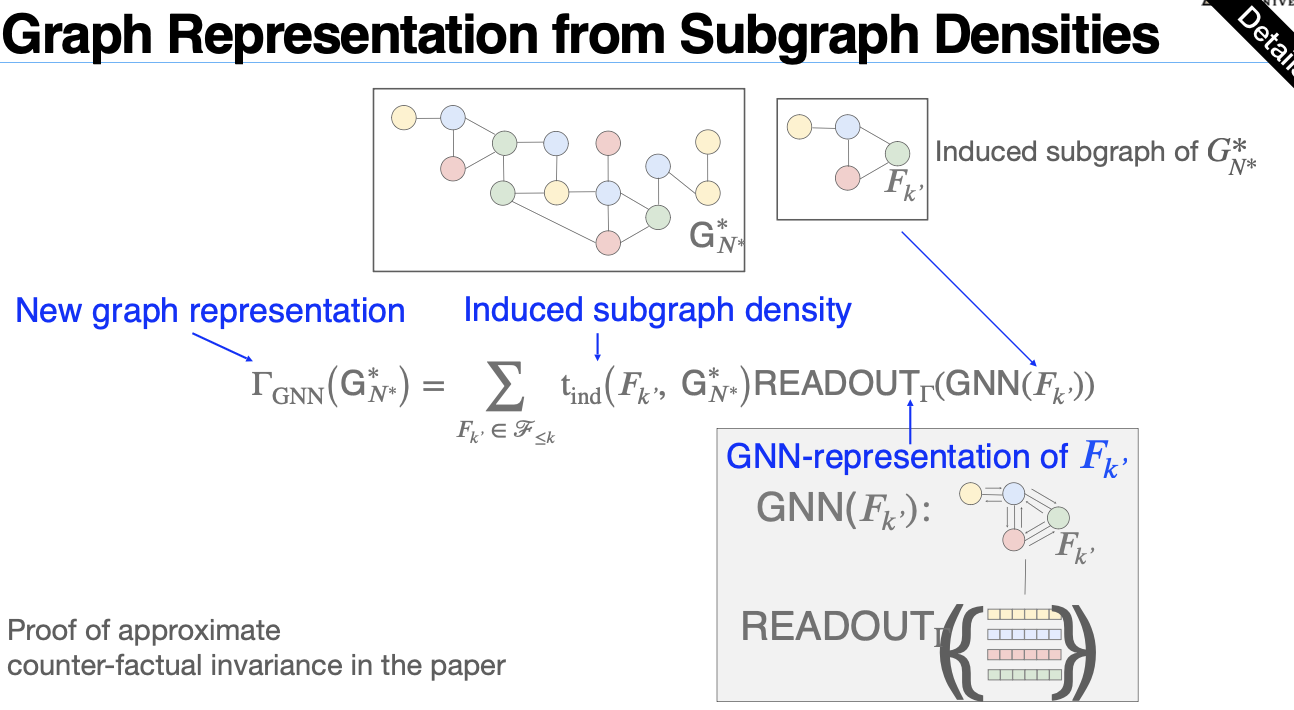
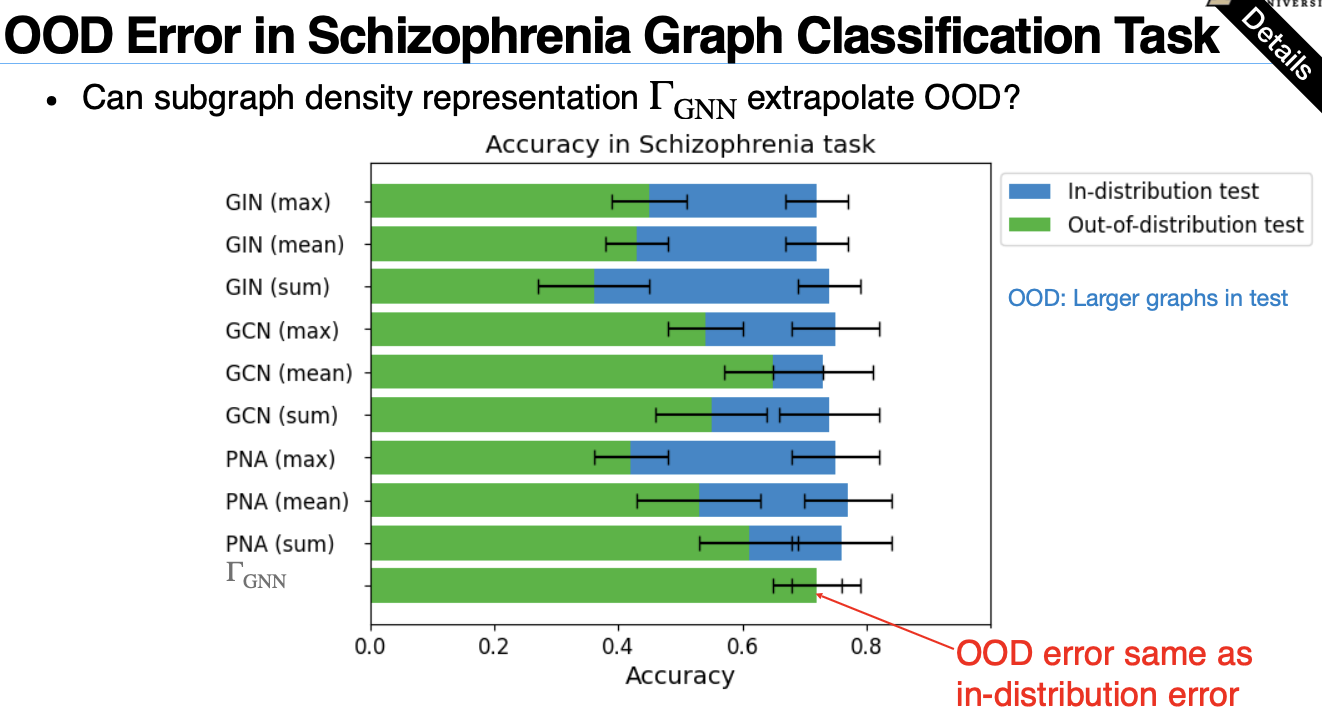
Link Prediction
Temporal Graph Representation Learning is Observational
- Equivalence between two temporal graph representation learning frameworks:
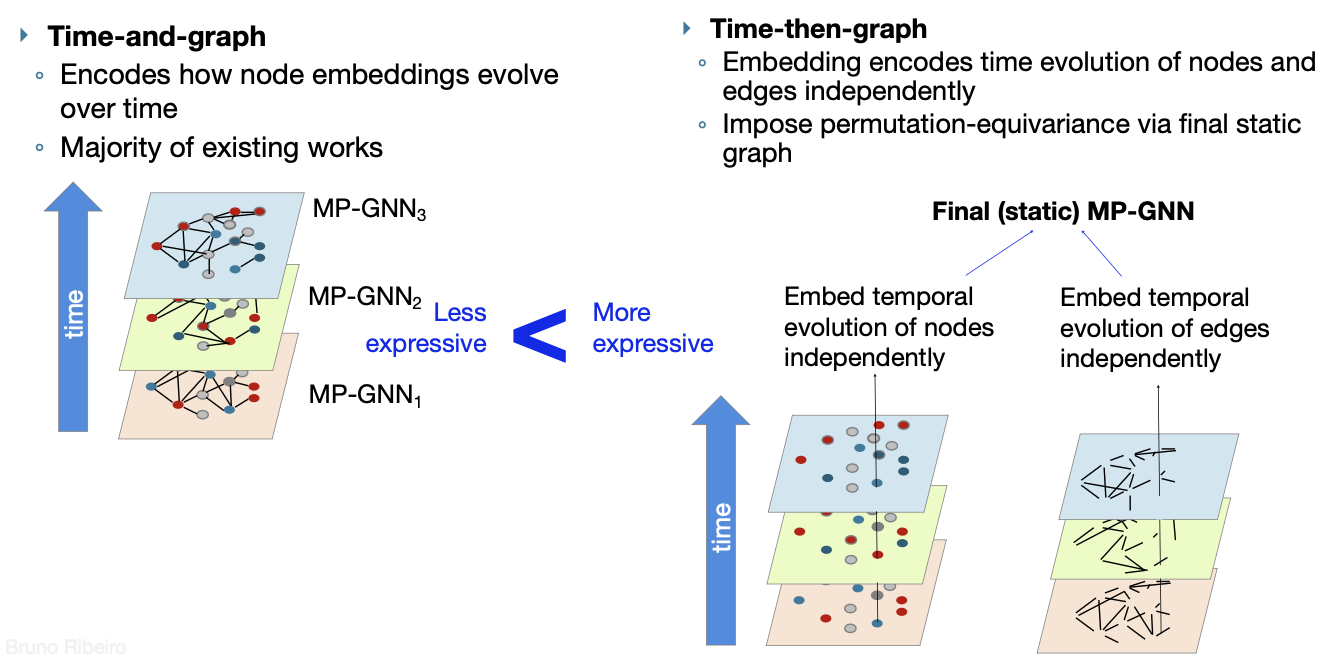
- Time-and-graph representations
- Time-then-graph representations
- In general, time-and-graph and time-then-graph are equally expressive
- Using Message Passing GNNs (MP-GNNs), time-then-graph are more expressive than time-and-graph
Time-then-graph more expressive than Time-and-graph (when using MP-GNNs)
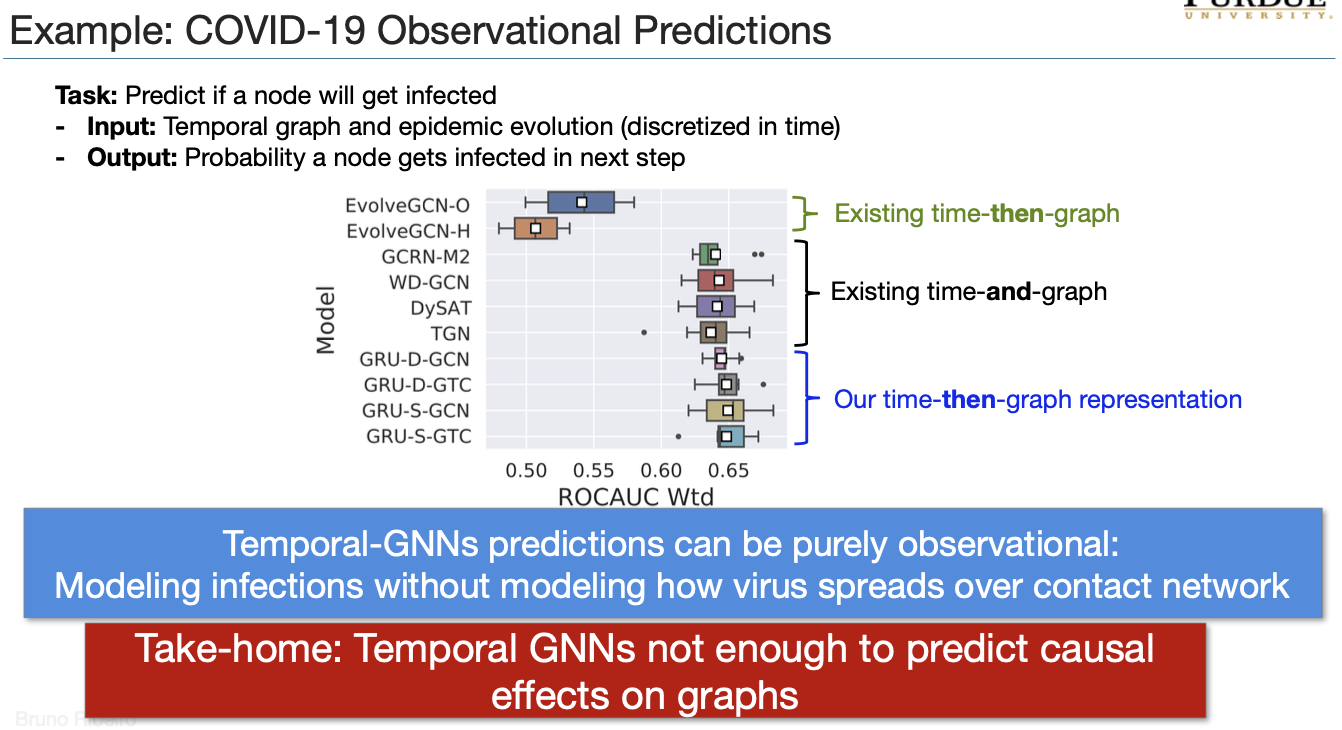
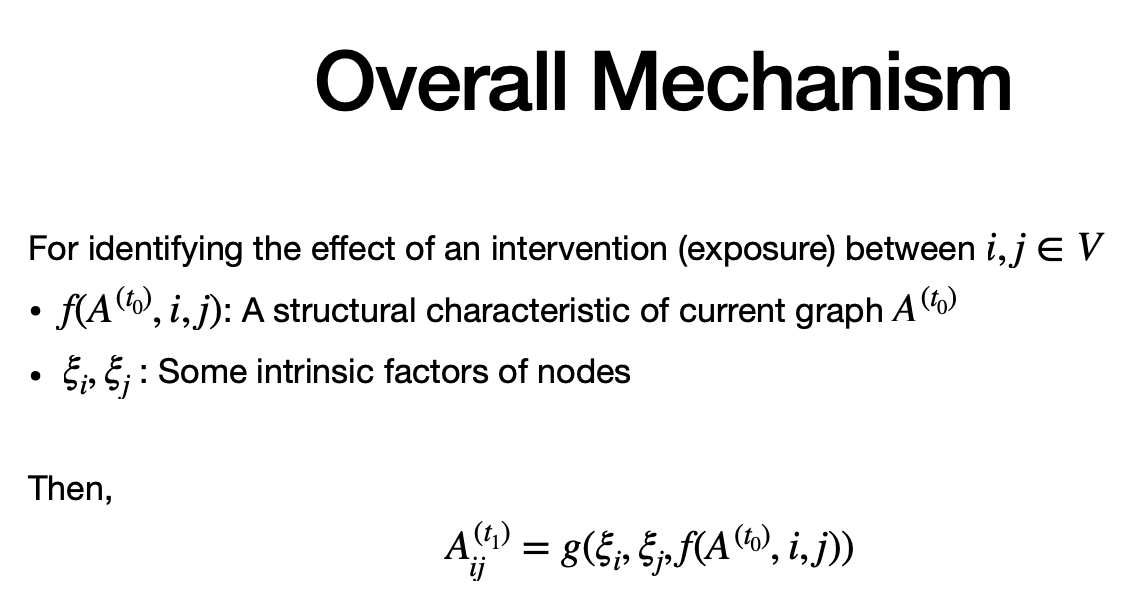
Causality & Link Prediction
Link Prediction as an exposure
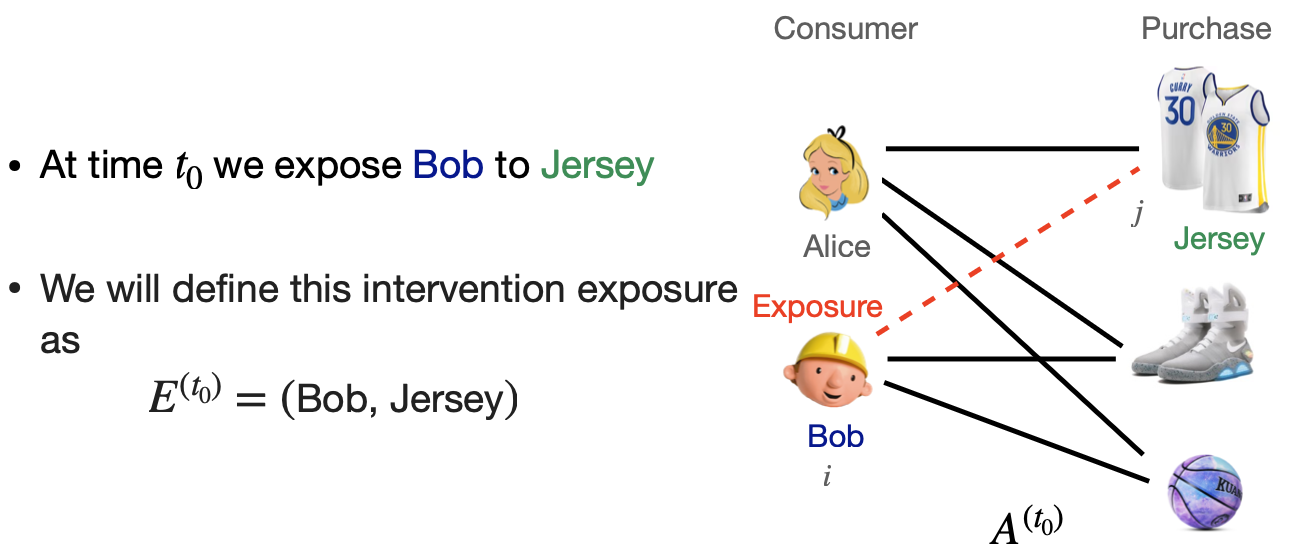
Task: Link Creation outcome
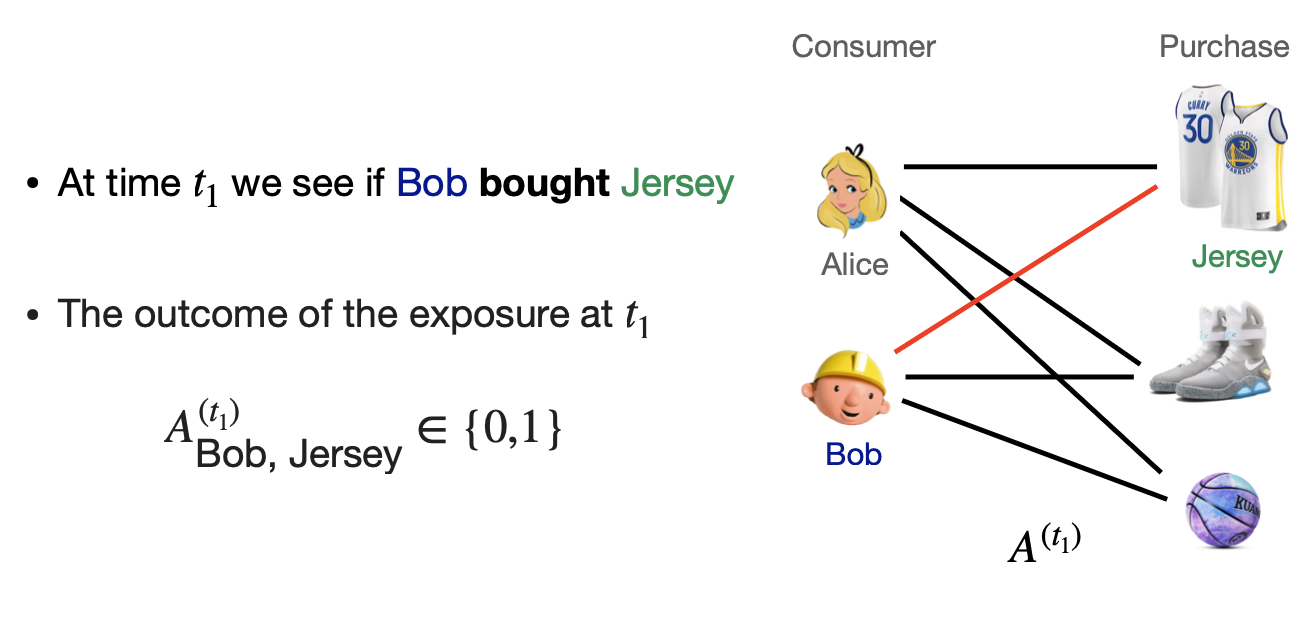
Causal Identifiability

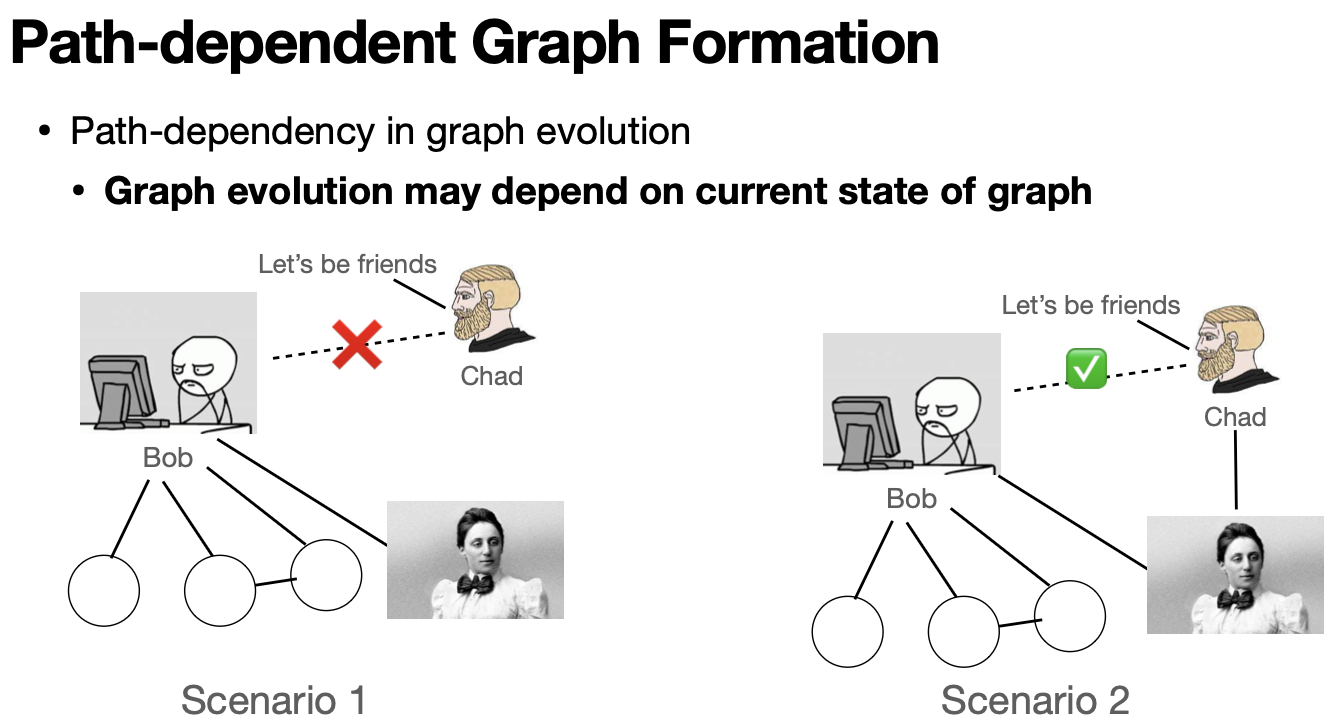
Graph Formation Process Key to Understand Effect of Exposures
Graph Formation Processes
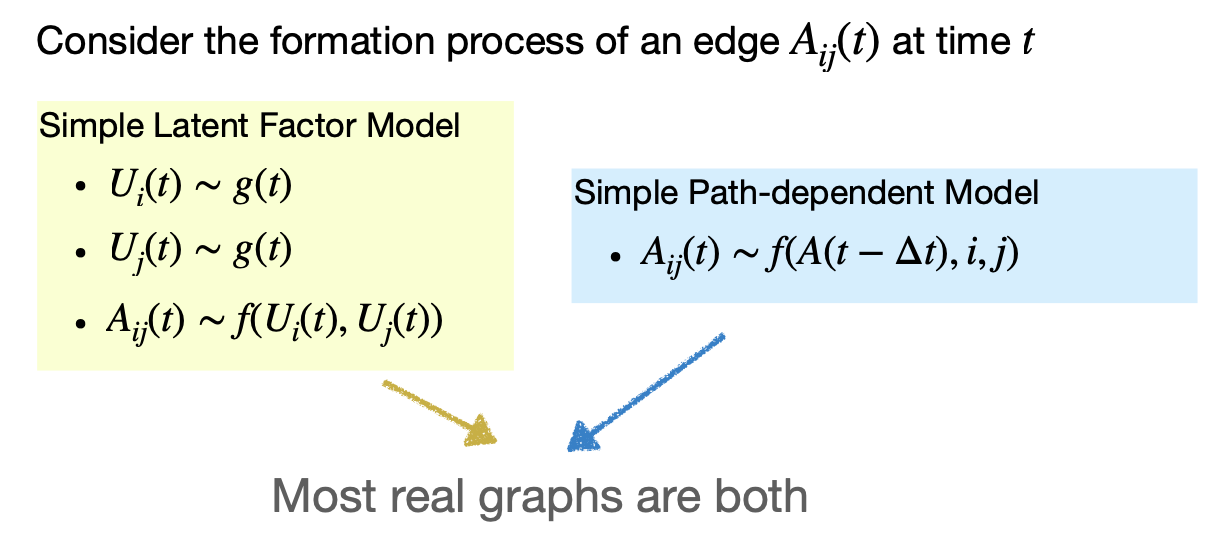
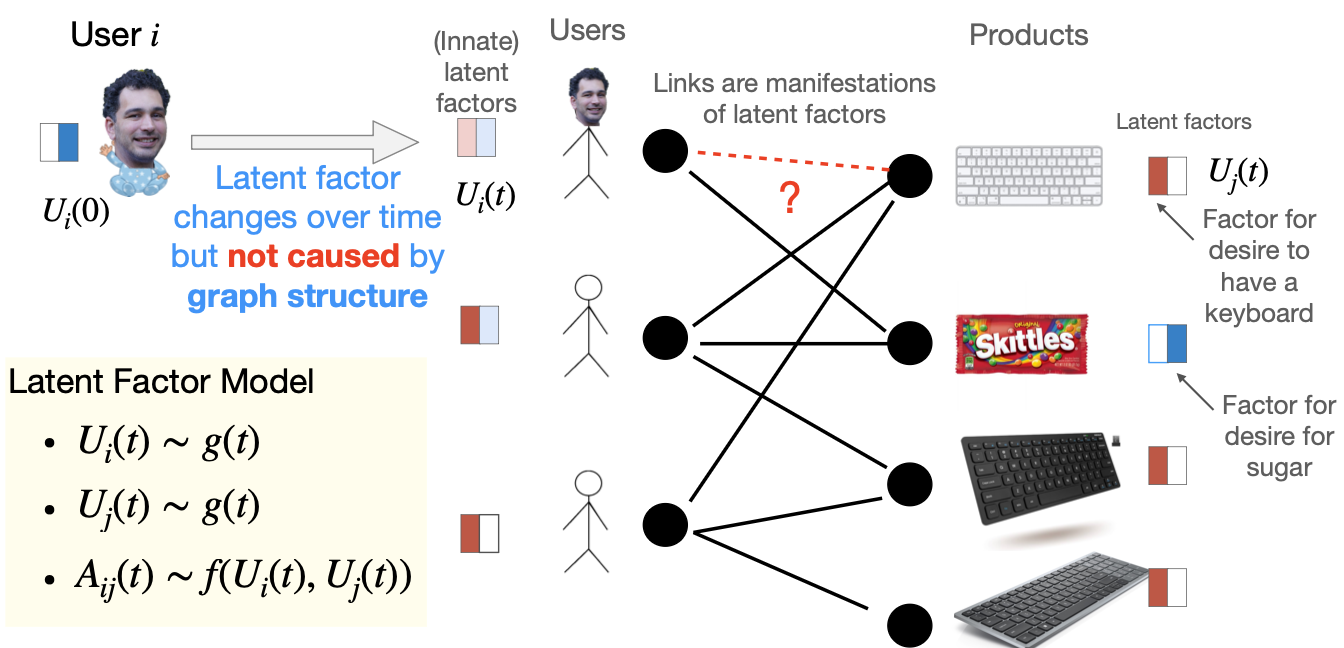
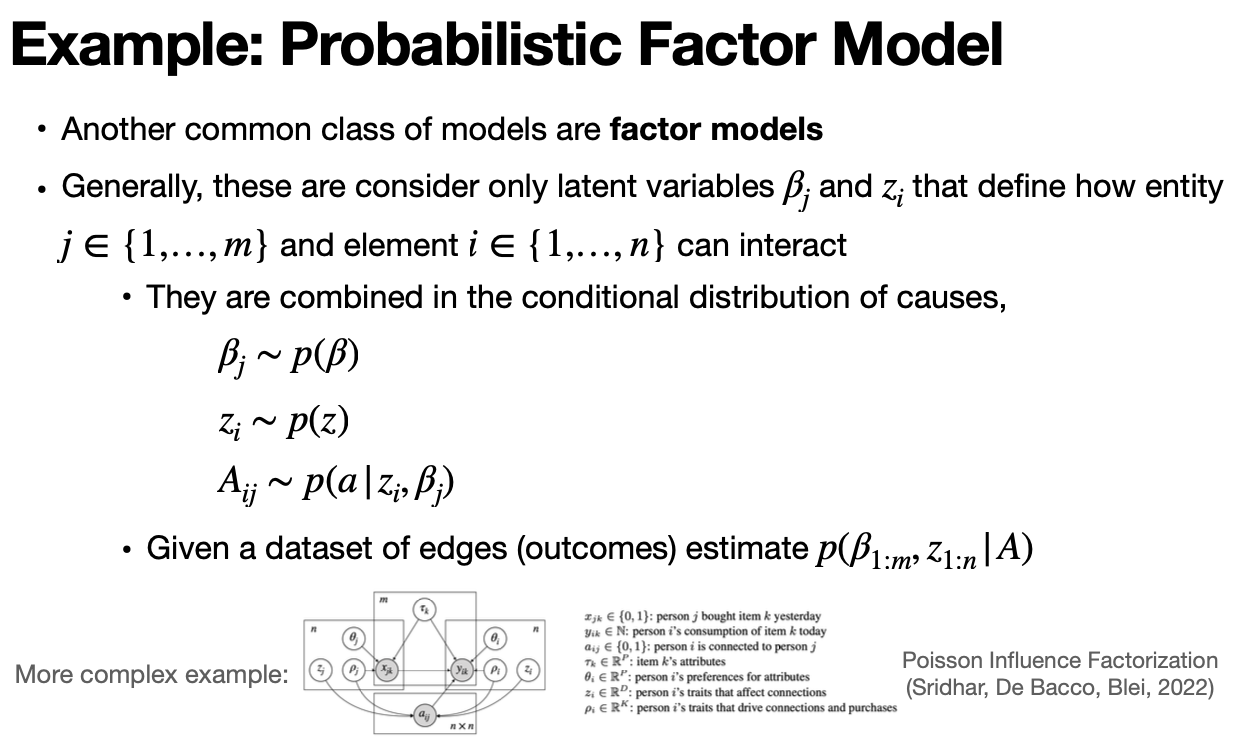
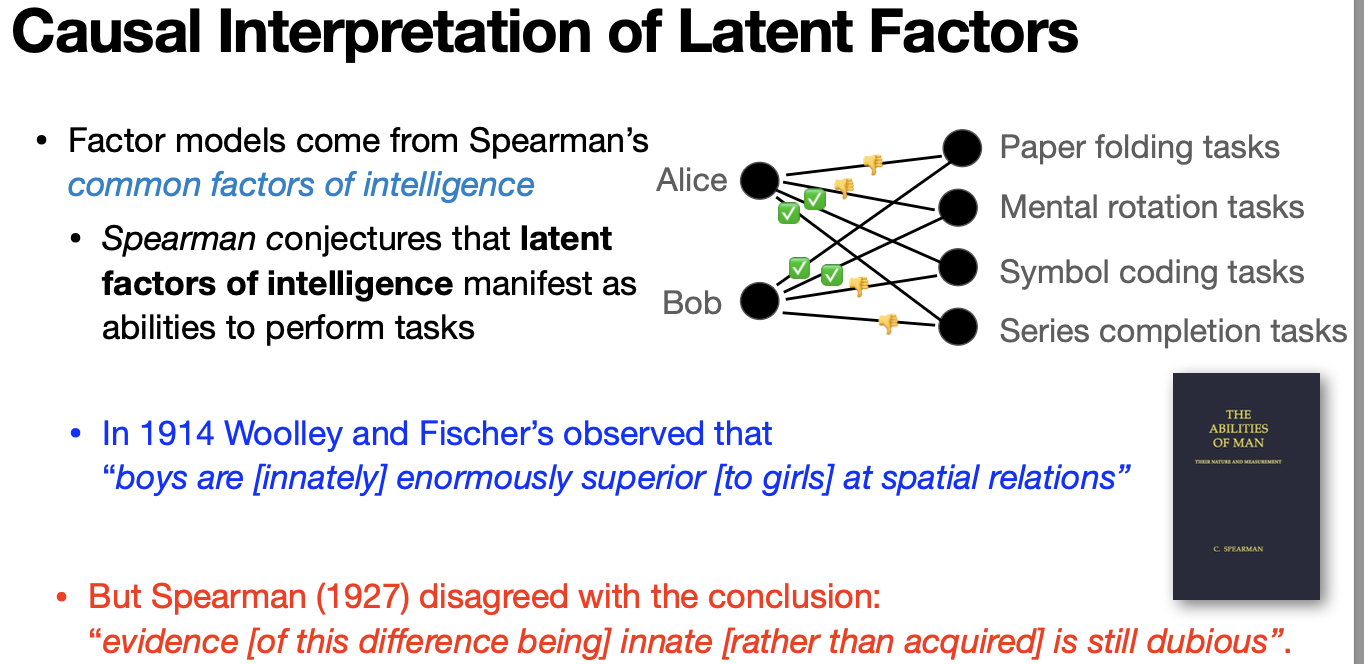
Latent Factor Graph Formation