CS224W-Machine Learning with Graph-Introduction
Introduction to Machine Learning for Graphs
Definition Graphs are a general language for describing and analyzing entities with relations/interactions.
图的数据种类:
Event Graphs, Computer Networks, Disease Pathways, Food Webs, Particle Networks, Underground Networks, Social Networks, Economic Networks, Communication Networks, Citation Networks, Internet, Networks of Neurons, Knowledge Graphs, Regulatory Networks, Scene Graphs, Code Graphs, Molecules, 3D Shapes.
Complex domains have a rich relational structure, which can be represented as a relational graph.
为什么图深度学习难?难点在哪里?
Networks are complex.
- Arbitrary size and complex topological structure(复杂的拓扑结构) (i.e, no spatial locality like grids)
- No fixed node ordering or reference point
- Often dynamic and have multimodal features
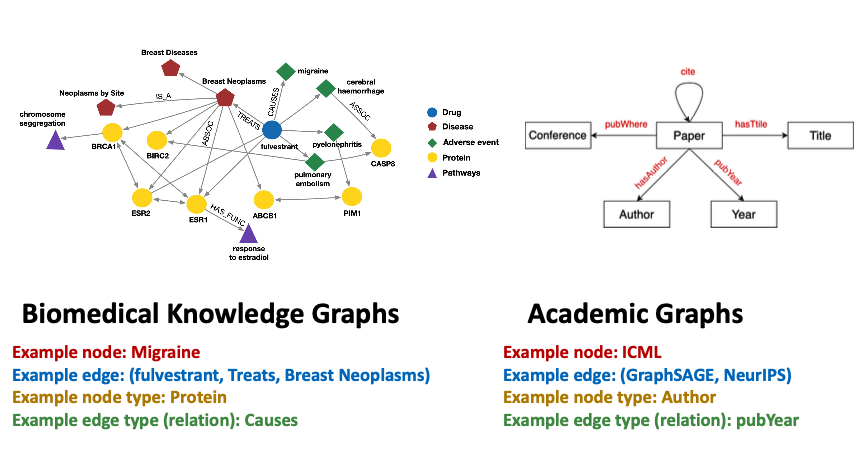
Definition A heterogeneous graph is defined as
- Nodes with node types
- Edges with relation types
- Node type
- Relation type
- Nodes and edges have attributes/features
Heterogeneous Graphs(异构图)
有向图和无向图 Directed vs. Undirected Graphs
Undirected
- Links: undirected (symmetrical, reciprocal)
Directed
- Links: directed
其他相关因素: Weights, Types, Properties, Attributes
二分图 Bipartite Graph
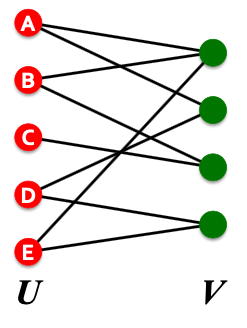
- Bipartite graph is a graph whose nodes can be divided into two disjoint sets and such that every link connects a node in to one in ; that is, and are independent sets.
- Examples
- Authors-to-Papers (they authored)
- Actors-to-Movies (they appeared in)
- Users-to-Movies (they rated)
- Recipes-to-Ingredients (they contain)
- “Folded” networks
- Author collaboration networks
- Movie co-rating networks
Graph Machine Learning Tasks
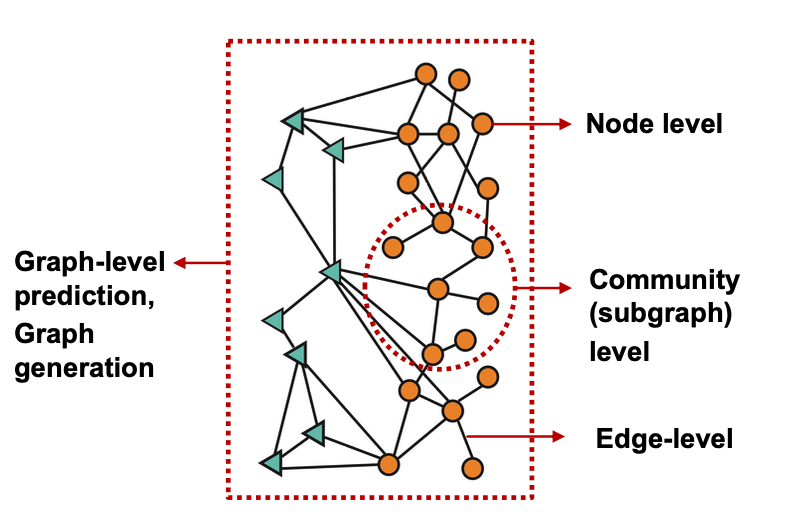
- Graph-level prediction, Graph generation
- Node level
- Community (subgraph) level
- Edge level
Graph Machine Learning Tasks
Node-Level Tasks
Node classification Example
Node-Level Network Structure
Goal: Characterize the structure and position of a node in the network
- Node degree (节点度)
- Node importance & position (重要性和位置)
- Number of shortest paths passing through a node
- Avg. shortest path length to other nodes
- Substructures around the node (节点的周围的结构)
Node’s Subgraphs: Graphlets (图基元, 类似于同一种形状的子图的数量)
Graphlets are defined as small induced subgraphs of a large network that appear at any frequency.
Graphlets: A count vector of rooted subgraphs at a given node.
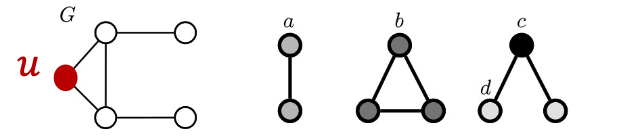
我们可以看到节点, 整个图, 所有的graphlets 的形状如右侧的3个小图。
So, Graphlets instances of node :
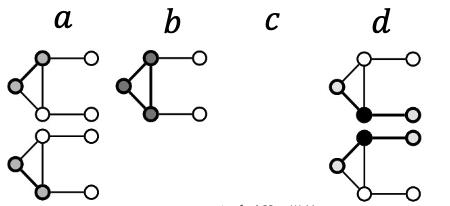
Graphlets of node :
Example: AlphaFold-Solving Protein Folding
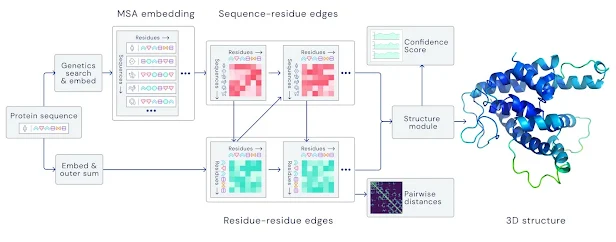
Key idea: “Spatial graph”
- Nodes: Amino acids in a protein sequence
- Edges: Proximity between amino acids (residues)
Link-Level Prediction Task
Link-level prediction task example
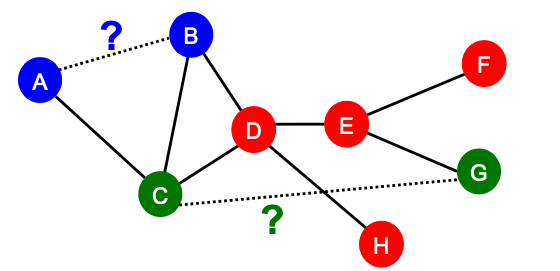
- The task is to predict new/missing/unknown links based on the existing links.
- At test time, node pairs (with no existing links) are ranked, and top node pairs are predicted.
- Task: Make a prediction for a pair of nodes.
图的边预测 (Link Prediction as a Task)
Two formulations of the link prediction task:
- Links missing at random:
Remove a random set of links and then aim to predict them
- Links over time:
Given a graph defined by edges up to time , output a ranked list of edges (not in ) that are predicted to appear in time
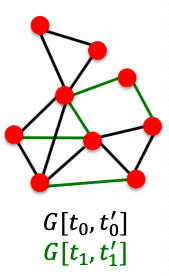
Evaluation:
- : # new edges that appear during the test period
- Take top elements of and count correct edges
Example 1: Recommender Systems
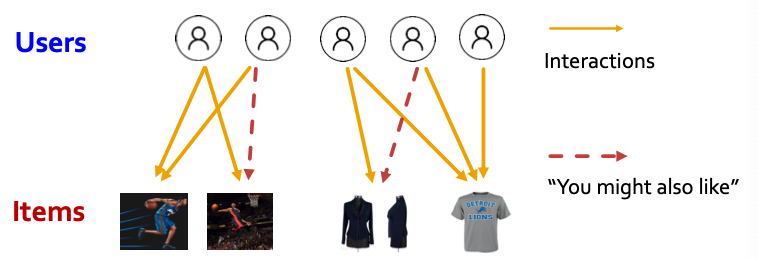
- Users interacts with items
- Watch movies, buy merchandise, listen to music
- Nodes: Users and items
- Edges: User-item interactions
- Goal: Recommend items users might like
Example 2: Biomedical Graph Link Prediction
Query: How likely will Simvastatin and Ciprofloxacin, when taken together, break down muscle tissue?
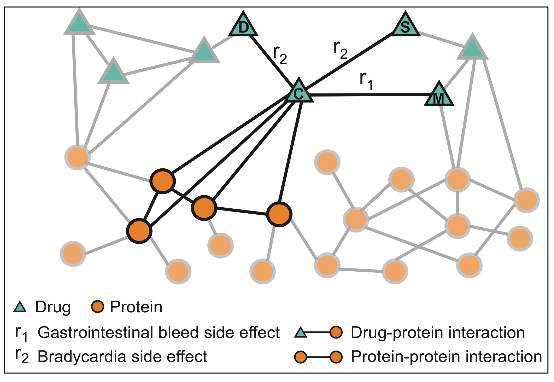
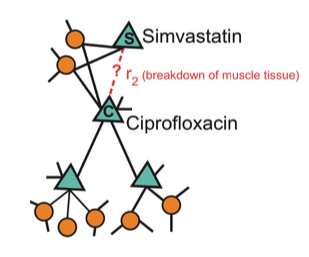
- Nodes: Drugs & Proteins
- Edges: Interaction
Graph-Level Tasks
Graph-Level Features
Goal: We want make a prediction for an entire graph or a subgraph of the graph.
Example: Road Network as a Graph
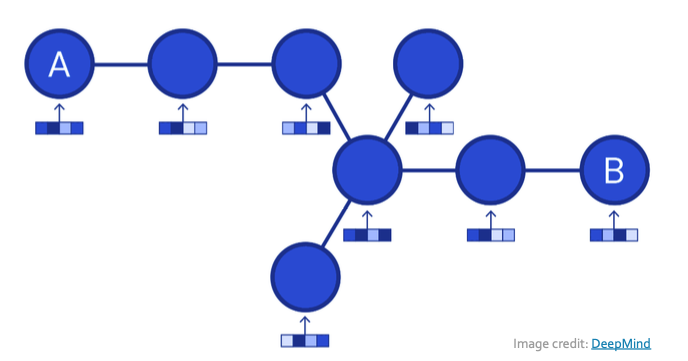
- Nodes: Road segments
- Edges: Connectivity between road segments
- Prediction: Time of Arrival (ETA)