CS224W-Machine Learning with Graph-Node Embeddings
Traditional ML for Graphs
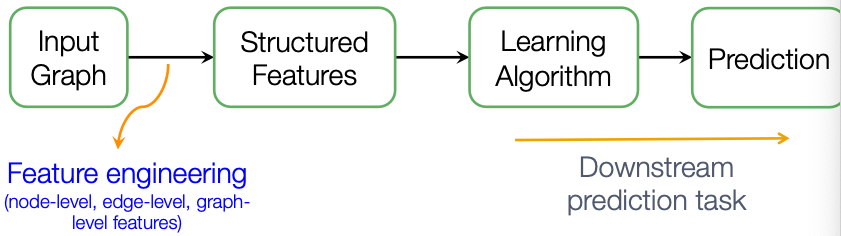
Given an input graph, extract node, link and graph-level features, then learn a model (SVM, neural network, etc.) that maps features to labels.
Graph Representation Learning(图表示学习)
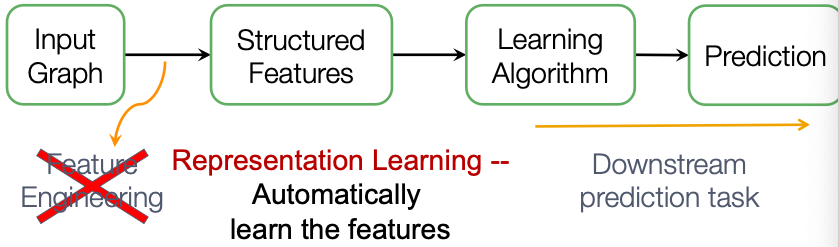
Graph Representation Learning alleviates the need to do feature engineering every single time.
Goal: Efficient task-independent feature learning for machine learning with graphs! (不需要特征学习)
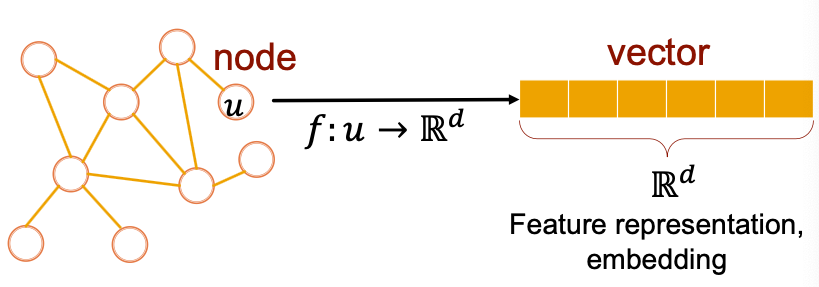
Why Embedding? (为什么需要嵌入?)
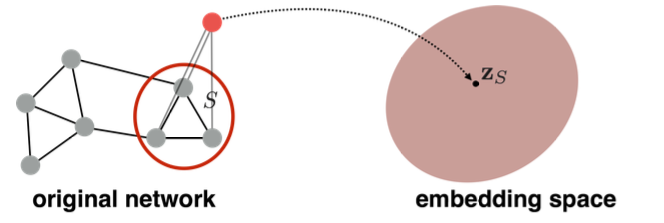
Task: Map nodes into an embedding space
- Similarity of embeddings between nodes indicates their similarity in the network.
- Both nodes are close to each other (connected by an edge)
- Encode network information
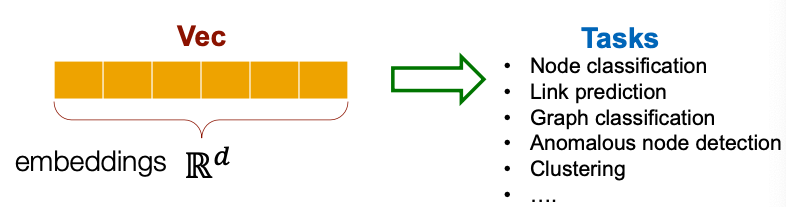
- Potentially used for many downstream predictions (可用于许多下游预测任务)
Encoder and Decoder
Setup
- is the vertex set.
- A is the adjacency matrix (assume binary)
Embedding Nodes
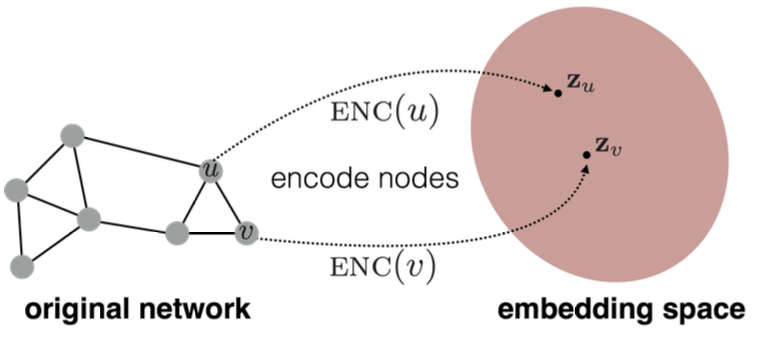
Goal is to encode nodes so that similarity in the embedding space (e.g., dot product) approximates similarity in the graph.
Learning Node Embedding (节点嵌入)
- Encoder maps from nodes to embeddings
- Define a node similarity function (i.e., a measure of similarity in the original network)
- Decoder maps from embeddings to the similarity score
- Optimize the parameters of the encoder to that
两个关键部分 Encoder + Decoder
- Encoder: maps each node to a low-dimensional vector
- node in the input graph
- d-dimensional embedding
- Similarity function: specifies how the relationships in vector space map to the relationships in the original network
- 左: Similarity of and in the original network
- 右: dot product between node embeddings
“Shallow” Encoding
Simplest encoding approach: Encoder is just an embedding-lookup
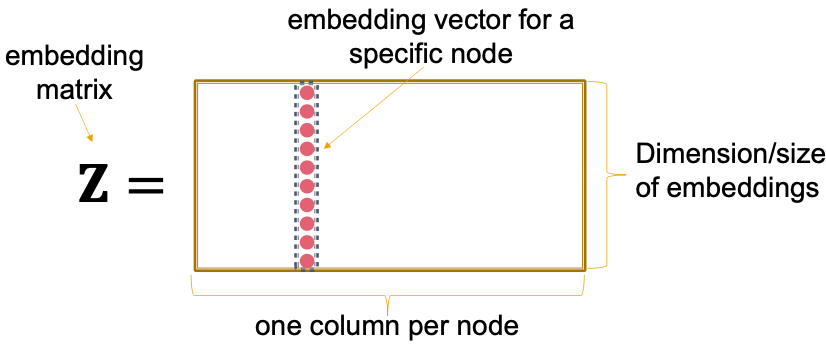
Matrix, each column is a node embedding [what we learn/ optimize]
Indicator vector, all zeroes except a one in column indicating node
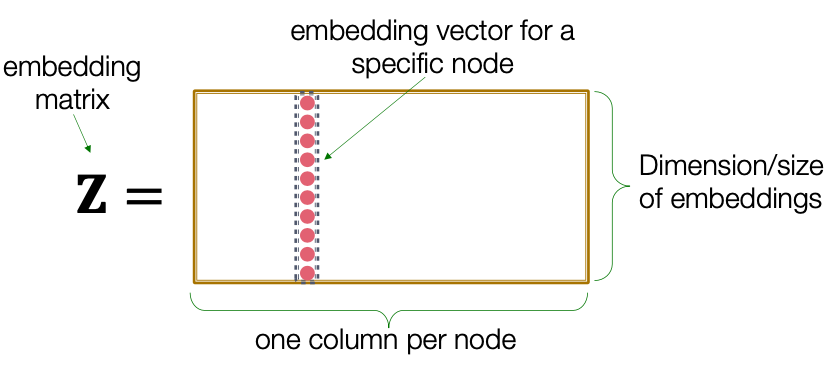
Each node is assigned a unique embedding vector
Framework Summary
- Encoder + Decoder Framework
- Shallow encoder: Embedding lookup
- Parameters to optimize: which contains node embeddings for all nodes
- We will cover deep encoders in the GNNs
- Decoder: based on node similarity
- Objective: maximize for node pairs that are similar
Random Walk Approaches for Node Embeddings
Notation
- Vector : The embedding of node (what we aim to find.)
- Probability : The (predicted) probability of visiting node on random walks starting from node .
Non-Linear functions used to produce predicted probabilities
- Softmax function: Turn vector of real values (model predictions) into probabilities that sum to :
- Sigmoid function: S-shaped function that turns real values into the range of . Written as
Random Walk
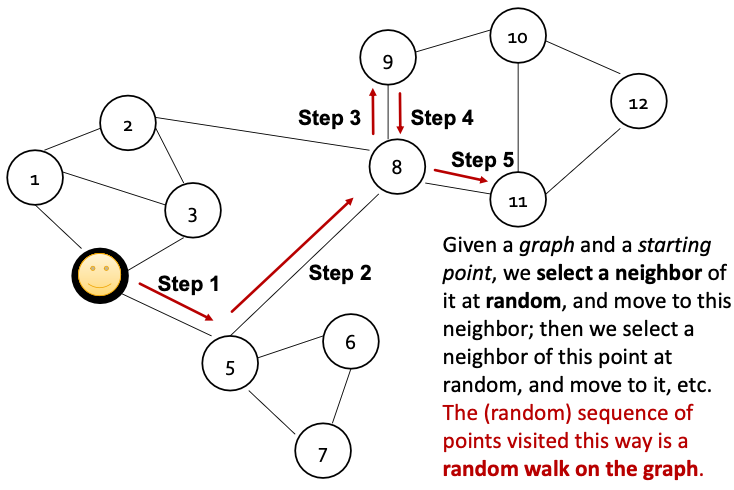
Random-Walk Embeddings
Random-Walk Embeddings
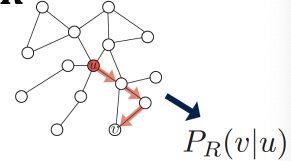
- Estimate probability of visiting node on a random walk starting from node using some random walk strategy .
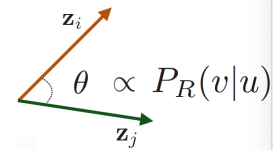
- Optimize embeddings to encode these random walk statistics
Similarity in embedding space (Here: dot product ) encodes random walk “similarity”
为什么使用随机步嵌入? (Why Random Walks?)
- Expressivity: Flexible stochastic definition of node similarity that incorporates both local and higher-order neighbourhood information.
- Efficiency: Do not need to consider all node pairs when training; only need to consider pairs that co-occur on random walks.
无监督特征学习 (Unsupervised Feature Learning)
- Intuition: Find embedding of nodes in space that preserves similarity.
- Idea: Learn node embedding such that nearby nodes are close together in the network.
- ? How do we define nearby nodes? neighbourhood of obtained by some random walk strategy .
Feature Learning as Optimization
- Given
- Our goal is to learn a mapping
- Log-likelihood objective:
- Given node , we want to learn feature representations that are predictive of the nodes in its random walk neighbourhood .
随机步优化(Random Walk Optimization)
- Run short fixed-length random walks starting from each node in the path using some random walk strategy
- For each node collect , the multiset of nodes visited on random walks starting from
- Optimize embeddings according to: Given node , predict its neighbours .
see Log-likelihood. 其中可以含有重复的节点。因为随机步可能多次到达相同的点。
直觉可以使用负对数似然估计。
- Parameterize using softmax:
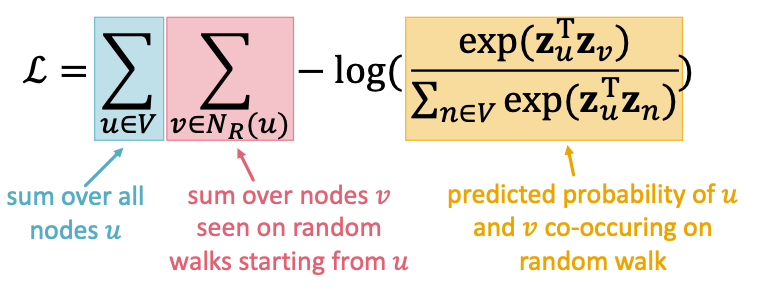
如果要这么计算耗费太高,如果使用别的方法解决这个问题?
Solution: Negative Sampling (负采样)
- Sample negative nodes each with probability. proportional to its degree.
- 关于负采样,需要考虑的两个方面
- Higher gives more robust estimates.
- Higher corresponds to higher bias on negative events
Stochastic Gradient Descent
How to we optimize (minimize) it?
Stochastic Gradient Descent: Instead of evaluating gradients over all examples, evaluate it for each individual training example.
- Initialize at some randomized value for all nodes .
- Iterate until convergence:
- Sample a node , for all calulate the gradient
- For all , update:
Node2vec Algorithm (Linear-time complexity + All 3 steps are individually parallelizable)
- Compute edge transition probabilities:
- For each edge we compute edge walk probabilities (based on ) of edge
- Simulate random walks of length starting from each node
- Optimize the node2vec objective using Stochastic Gradient Descent
Embeddings Entire Graphs
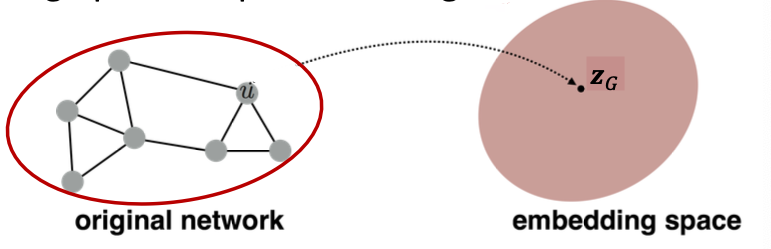
Goal: Want to embed a subgraph or an entire graph . Graph embedding: .
- Approach 1 ( 简单但是有效奥)
- Run a standard graph embedding technique on the (sub)graph
- Then just sum (or average) the node embeddings in the (sub)graph
- Approach 2
- Introduce a “virtual node” to represent the (sub)graph and run a standard graph embedding technique
Hierarchical Embeddings
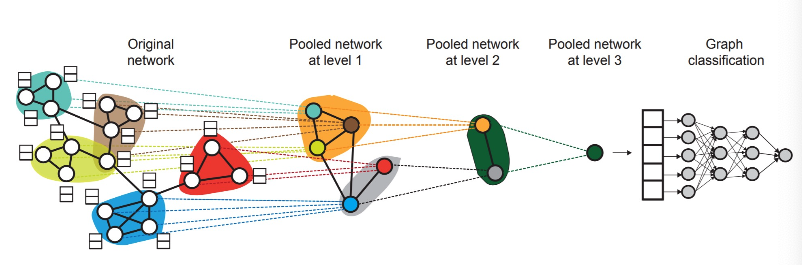
DiffPool: We can also hierarchically cluster nodes in graphs, and sum/average the node embeddings according to these clusters.
Matrix Factorization and Node Embeddings (矩阵分解和节点嵌入)
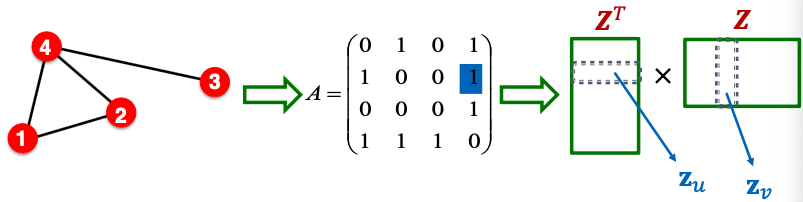
Connection to Matrix Factorization
- Simplest node similarity: Node are similar if they are connected by an edge.
- This means: , which is the entry of the graph adjacency matrix
- Therefore,
其他矩阵分解相关内容可见 (Applied Linear Algebra for Data Science Lecturenotes)
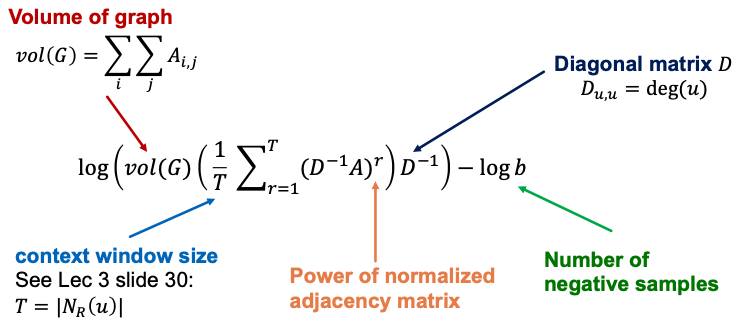
Random Walk - based Similarity
- DeepWalk and node2vec have a more complex node similarity definition based on random walks
- DeepWalk is equivalent to matrix factorization of the following complex matrix expression:
Explanation of this equation
How to use Embeddings ? (怎么嵌入?)
- Clustering/Community detection: Cluster points .
- Node classification: Predict label of node based on
- Link Prediction: Predict edge based on
- Where we can: concatenate, average, product, or take a difference between the embeddings:
- Concatenate:
- Hadamard: per coordinate product
- Sum/Average:
- Distance:
- Where we can: concatenate, average, product, or take a difference between the embeddings:
- Graph classification: Graph embedding via aggregating node embeddings or virtual-node. Predict label based on graph embedding