CS224W-Machine Learning with Graph-Heterogeneous
How to handle graphs with multiple nodes or edge types (a.k.a heterogeneous graphs)?
Goal: Learning with heterogeneous graphs
- Relational GCNs
- Heterogeneous Graph Transformer
- Design space for heterogeneous GNNs
Motivation
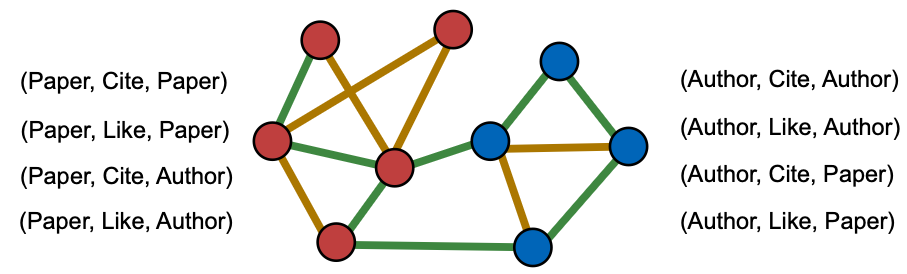
- 2 types of nodes:
- Node type A: Paper nodes
- Node type B: Author nodes
- 2 types of edges:
- Edge type A: Cite
- Edge type B: Like
- 2 types of nodes + 2 types of edges
- Relation types: (node_start, edge, node_end)
- We use relation type to describe an edge (as opposed to edge type)
- Relation type better captures the interaction between nodes and edges
A heterogeneous graph is defined as
- Nodes with node types
- Node type for node
- Edges with edge types (An edge can be described as a pair of nodes)
- Edge type for edge
- Relation type for edge is a tuple:
There are other definitions for heterogeneous graphs as well - describe graphs with node & edge types.
Observation: We can also treat types of nodes and edges as features
- Example: Add a one-hot indicator for nodes and edges
- Append feature to each “author node”; Append feature to each “paper node”
- Similarly, we can assign edge features to edges with different types.
- Then, a heterogeneous graph reduces to a standard graph
When do we need a heterogeneous graph?
- Case 1: Different node/edge types have different shapes of features
- An “author node” has 4-dim feature, a “paper node” has 5-dim feature
- Case 2: We know different relation types represent different types of interactions
- (English, translate, French) and (English, translate, Chinese) require different models
Heterogeneous graph is a more expressive graph representation!
- Captures different types of interactions between entities.
But it also comes with costs
- More expensive (computation, storage)
- More complex implementation
There are many ways to convert a heterogeneous graph to a standard graph(that is, a homogeneous graph(同构))
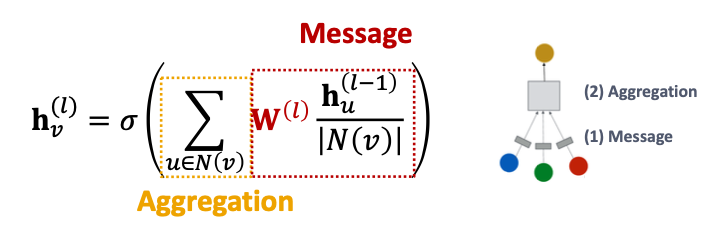
- Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN)
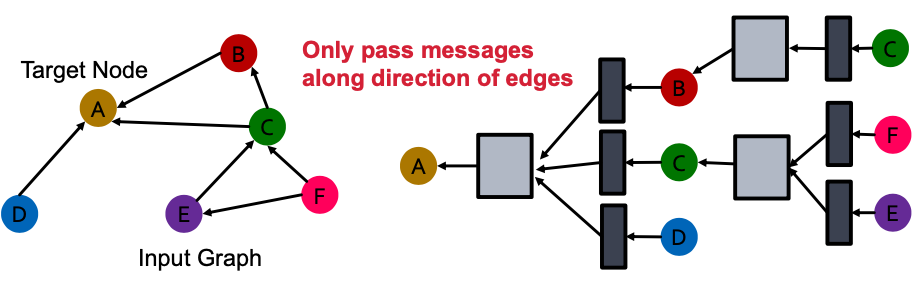
- How to write this as Message + Aggegation?
We will extend GCN to handle heterogeneous graphs with multiple edge /relation types
We stat with a directed graph with one relation
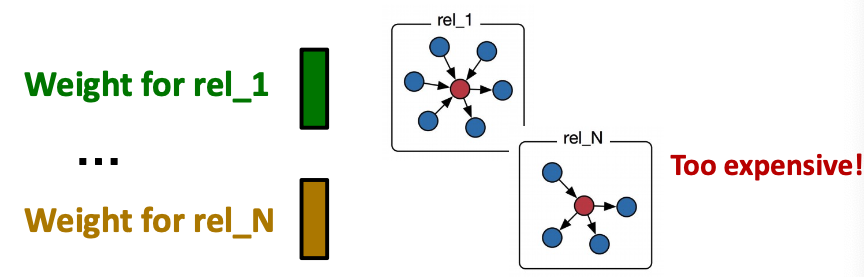
What is the graph has multiple relation types?
- Use different neural network weights for different relation types.
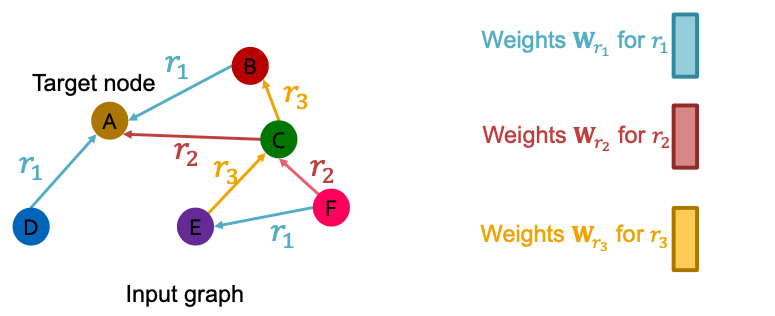
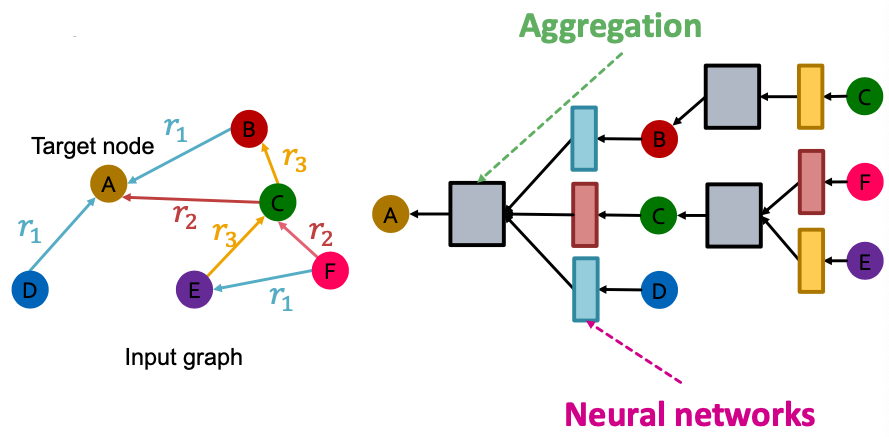
- Introduce a set of neural networks for each relation type!
Relational GCN: Definition
- Relational GCN(RGCN):
- How to write this as Message + Aggregation?
Normalized by node degree of the relation
- Message:
- Each neighbor of a given relation:
- Self-loop:
- Aggregation:
- Sum over messages from neighbors and self-loop, then apply activation
-
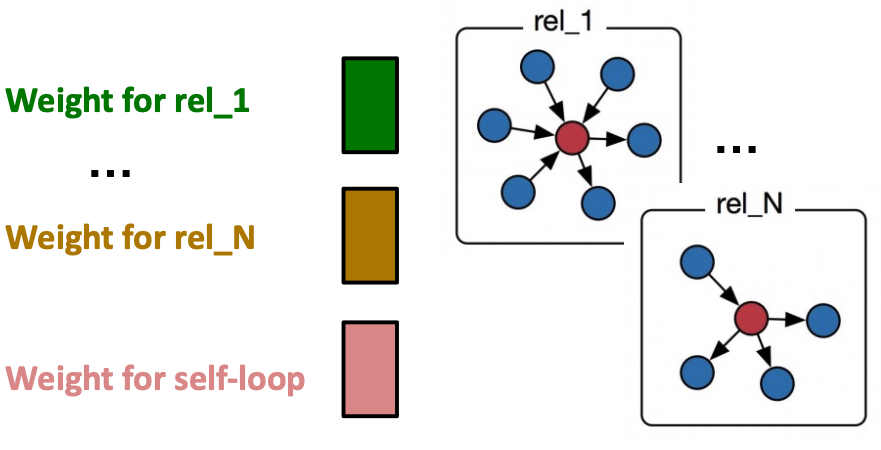
RGCN: Scalability (可扩展性)
- Each relation has matrices:
- The size of each is
- is the hidden dimension in layer
- Rapid growth of the number of parameters w.r.t number of relations! - Overfitting becomes an issue.
- Two methods to regularize the weights
- Use block diagonal matrices
- Key insight: make the weights spare!
- Use block diagonal matrices for
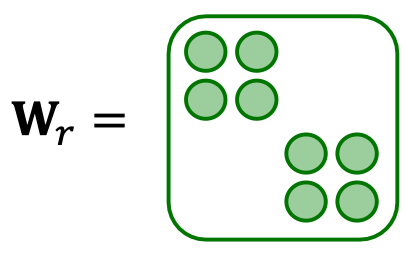
- Limitation: only nearby neurons/dimensions can interact through
- If use low-dimensional matrices, then # param reduces form to
- Basis/Dictionary learning
- Key insight: Share weights across different relations!
- Represent the matrix of each relation as a linear combination of basis transformations , where is shared across all relations
- are the basis matrices
- is the importance weight of matrix
- Now each relation only needs to learn , which is scalars
- Use block diagonal matrices
- Goal: Predict the label of a given node
- RGCN uses the representation of the final layer:
- If we predict the class of node from classes
- Take the final layer (prediction head): , each item in represents the probability of that class
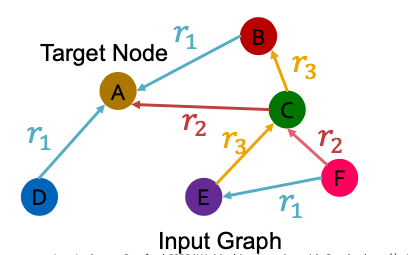
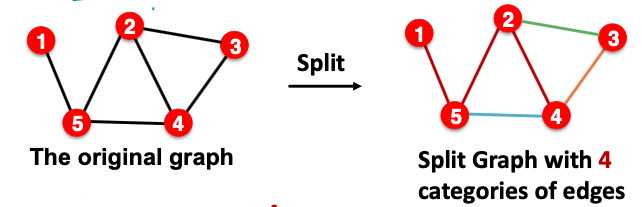
- Link prediction split:
- Every edge also has a relation type, this is independent of the 4 categories.
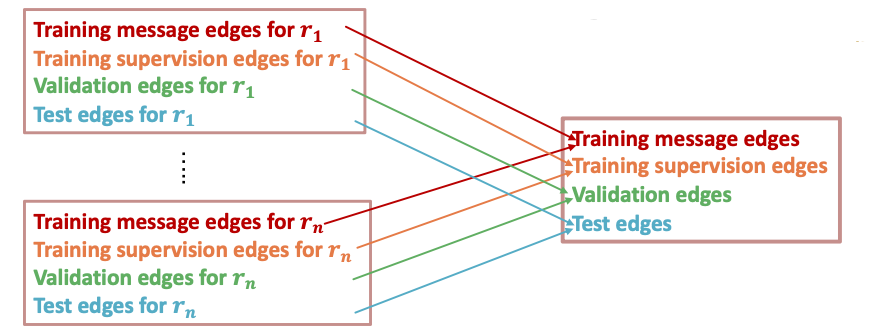
……更详细内容见其他。
Benchmark for Heterogeneous Graphs
Summary of RGCN
- Relational GCN, a graph neural network for heterogeneous graphs.
- Can perform entity classification as well as link prediction tasks.
- Ideas can easily be extended into RGCN (RGraphSAGE, RGAT, etc.)
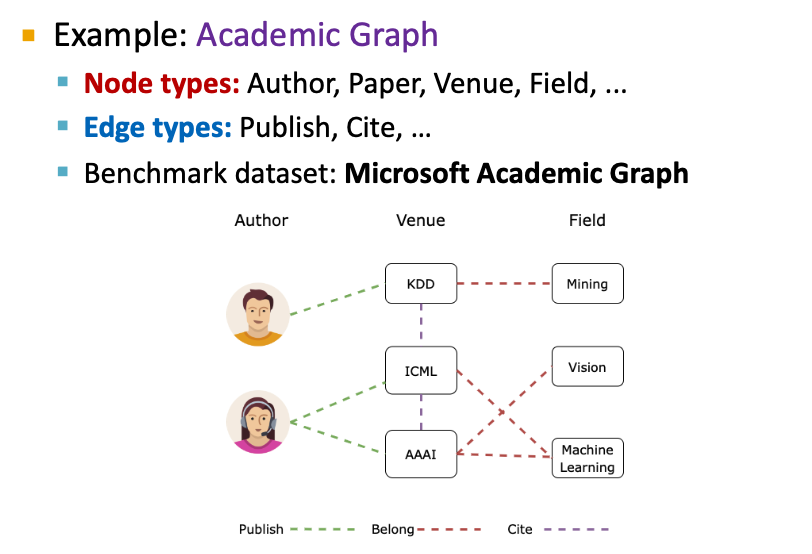
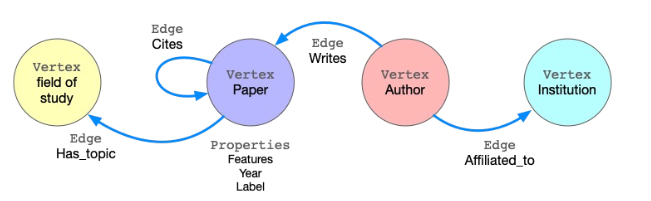
- Benchmark: ogbn-mag from Microsoft Academic Graph, to predict paper venues
Heterogeneous Graph Transformer
Graph Attention Networks(GAT)
Not all node’s neighbors are equally important
- Attention is inspired by cognitive attention.
- The attention focuses on the important parts of the input data and fades out the rest.
- Idea: the NN should devote more computing power on that small but important part of the data.
Heterogeneous Graph Transformer
- Motivation: GAT is unable to represent different node & different edge types.
- Introduce a set of neural networks for each relation type is too expensive for attention
- Recall: relation describes (node_s, edge, node_e)
Basics: Attention in Transformer
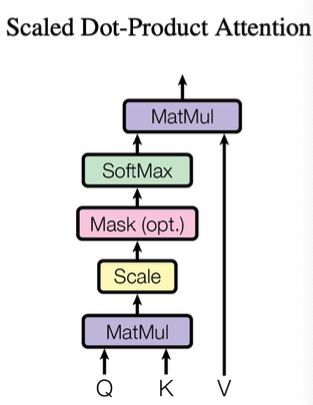
- HGT uses Scaled Dot-Product Attention (proposed in Transformer)
- Query: , key: , Value:
- have shape (batch_size, dim)
How do we obtain ?
- Apply Linear layer to the input
-
-
-
Heterogeneous Mutual Attention
Recall: Applying GAT to a homogeneous graph
- is the -th layer representation:
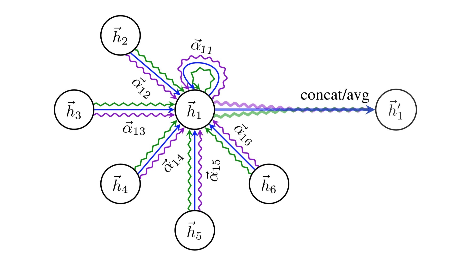
- Innovation: Decompose heterogeneous attention to Node- and edge-type dependent attention mechanism
- 3 node weight matrices, 2 edge weight matrices
- Without decomposition: relation types weight matrices (suppose all relation types exist)
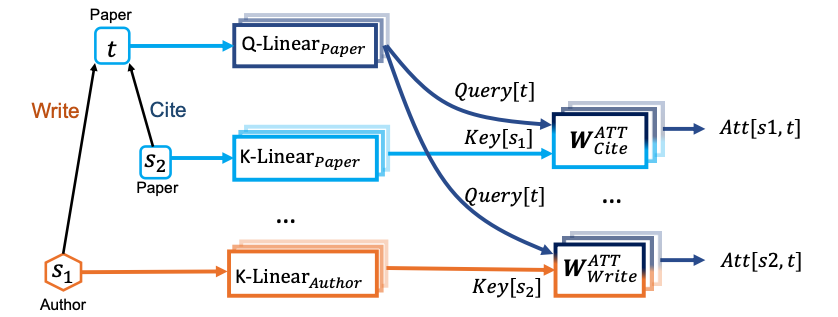
- Heterogeneous Mutual Attention:
- Each relation has a distinct set of projection weights
- : type of node , : type of edge
- & parameterize & , which further return Key and Query vectors &
- Edge type directly parameterizes
A full HGT layer
Similarly, HGT decomposes weights with node & edge types in the message computation
- : Weights for each node type
- : Weights for each edge type
Heterogeneous message computation
- Message function
- Observation: A node could receive multiple types of messages.
- Idea: Create a different message function for each relation type
- , is the relation type between node that sends the message, edge type , and node that receive the message
- Example : A Linear layer:
Heterogeneous Aggregation
- Heterogeneous Aggregation
- Observation: Each node could receive multiple types of message from its neighbors, and multiple neighbors may belong to each message type.
- Idea: We can define a 2-stage message passing
-
- Given all the messages sent to a node
- Within each message type, aggregation the messages that belongs to the edge typee with
- Aggregate across the edge types with
- Example:
Heterogeneous GNN Layers
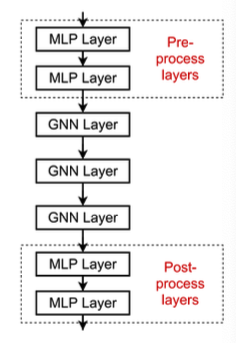
- Heterogeneous pre/post-process layers:
- MLP layers with respect to each node type
- Since the output of GNN are node embeddings
-
- is the type of node
- MLP layers with respect to each node type
- Other successful GNN designs are also encouraged for heterogeneous GNNs: Skip connections, batch/layer normalization, …
Heterogeneous Graph Manipulation
- Graph Frature manipulation
- 2 Common options: compute graph statistics (e.g., node degree) within each relation type, or across the full graph (ignoring the relation types)
- Graph Structure manipulation
- Neighbor and subgraph sampling are also common for heterogeneous graphs.
- 2 Common options: sampling within each relation type (ensure neighbors from each type are covered), or sample across the full graph.
Heterogeneous Prediction Heads
- Node-level prediction
- Edge-level prediction
- Graph-level prediction