Knowledge Graph Embeddings Heterogeneous graphs: a graph with multiple relation types.
Knowledge in graph from: capture entities, types, and relationships
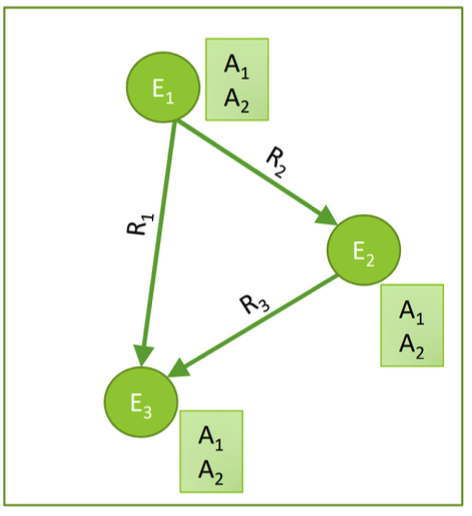
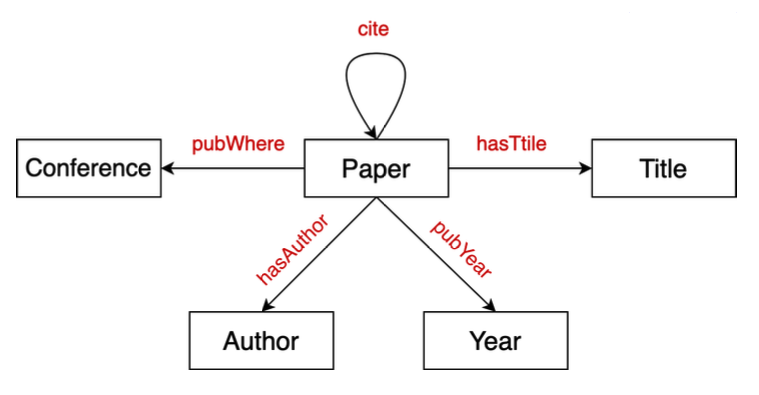
Nodes are labeled with their types. Edges between two nodes capture relationships between entities. Knowledge graph is an example of a heterogeneous graph. KG Example \text{KG Example} KG Example Bibiographic Networks
Node types: paper, title, author, conference, year Relation types: pubWhere, pubYear, hasTitle, hasAuthor, cite
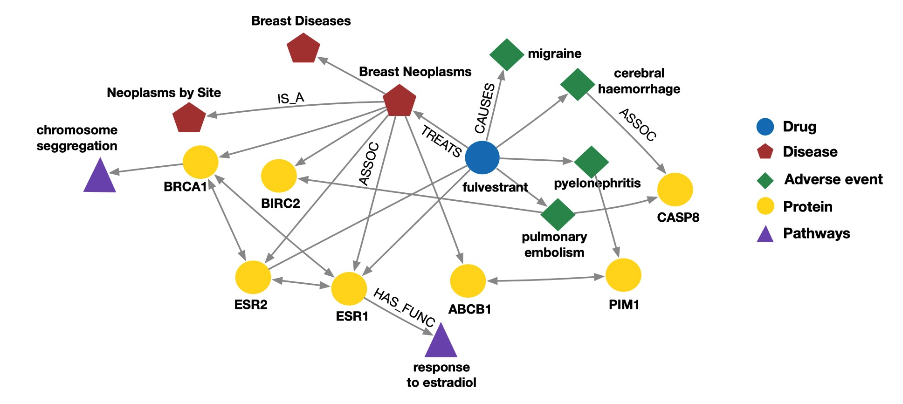
Bio Knowledge Graphs
Node types: drug, disease, adverse event, protein, pathway Relation types: has_func, causes, assoc, treats, is_a
Applications of Knowledge Graphs
Question answering and conversation agents
Knowledge Graph Dataset
Publicly available KGs:FreeBase, Wikidata, Dbpedia, YAGO, NELL, etc. Common characteristics:Massive: Millions of nodes and edges Incomplete: Many. true edges are missing
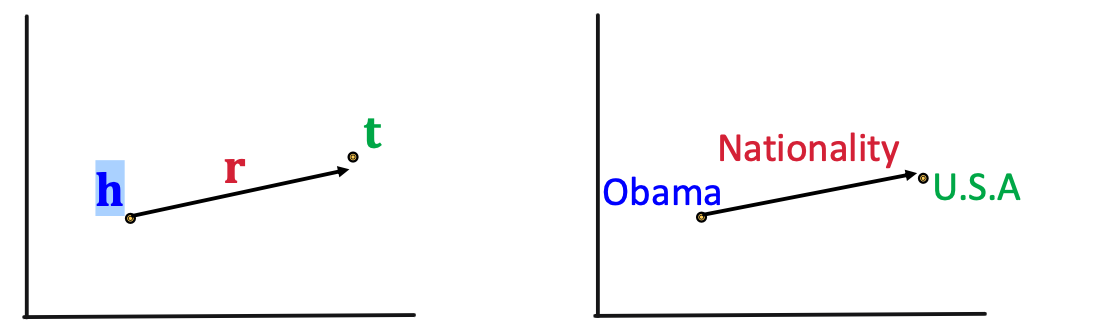
Knowledge Graph Completion KG Representation Edge in KG are represented as triples ( h , r , t ) (h,r,t) ( h , r , t ) head ( h ) (h) ( h ) ( r ) (r) ( r ) ( t ) (t) ( t ) Key Idea:Model entities and relations in embedding space R d \mathbb{R}^d R d Associate entities and relations with shallow embeddings (we do not learn a GNN here!) Given a triple ( h , r , t ) (h,r,t) ( h , r , t ) ( h , r ) (h,r) ( h , r ) t t t How to embed ( h , r ) (h,r) ( h , r ) How to define score f r ( h , t ) f_r(h,t) f r ( h , t ) Score f r f_r f r ( h , r , t ) (h,r,t) ( h , r , t ) f r f_r f r
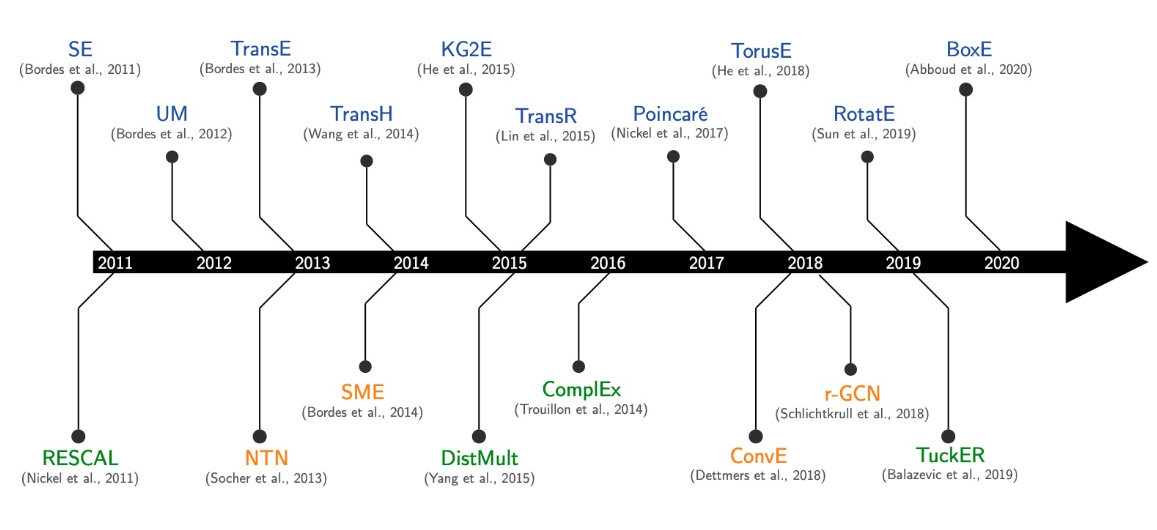
Many KG Embedding Models \text{Many KG Embedding Models} Many KG Embedding Models
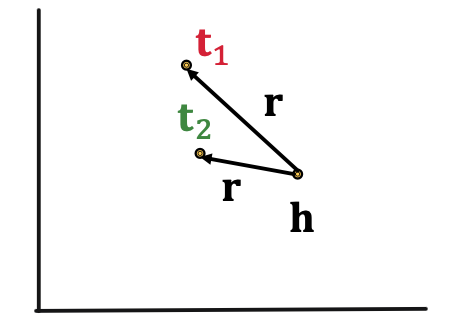
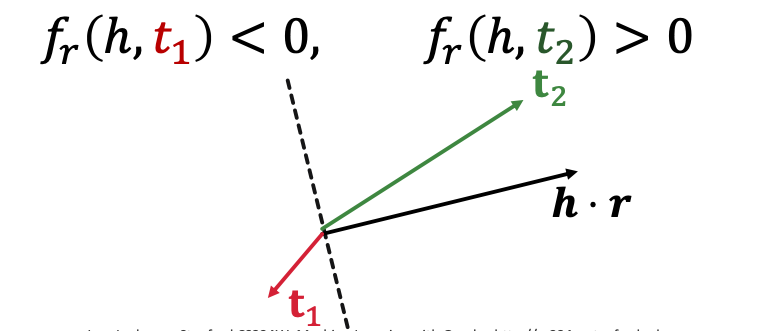
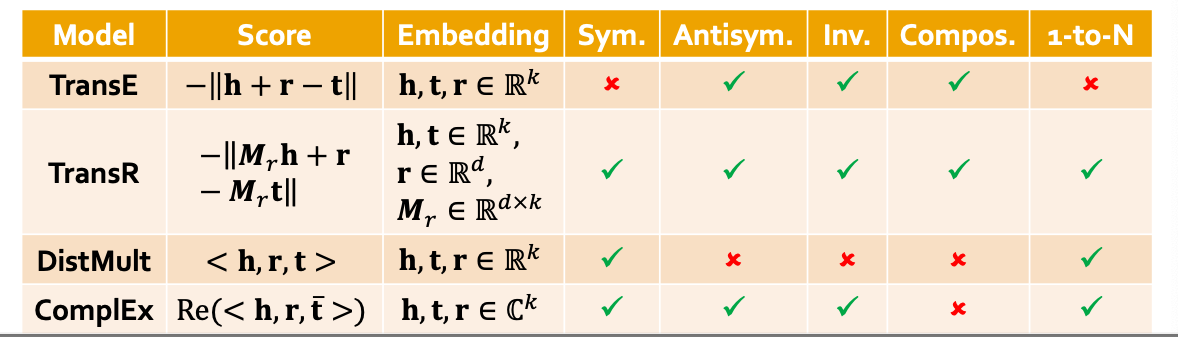
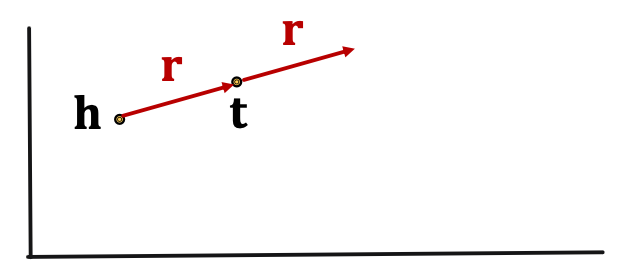
Knowledge Graph Completion: TransE Intuition: TranslationFor a triple ( h , r , t ) (h,r,t) ( h , r , t ) h,r,t ∈ R d \textbf{h,r,t} \in \mathbb{R}^d h,r,t ∈ R d TransE: h + r ≈ t \textbf{h} + \textbf{r} \approx \textbf{t} h + r ≈ t h + r ≠ t \textbf{h} + \textbf{r} \neq \textbf{t} h + r = t Entity scoring function: f r ( h , t ) = − ∣ ∣ h + r − t ∣ ∣ f_r(h,t) = -||\textbf{h}+\textbf{r}-\textbf{t}|| f r ( h , t ) = − ∣∣ h + r − t ∣∣
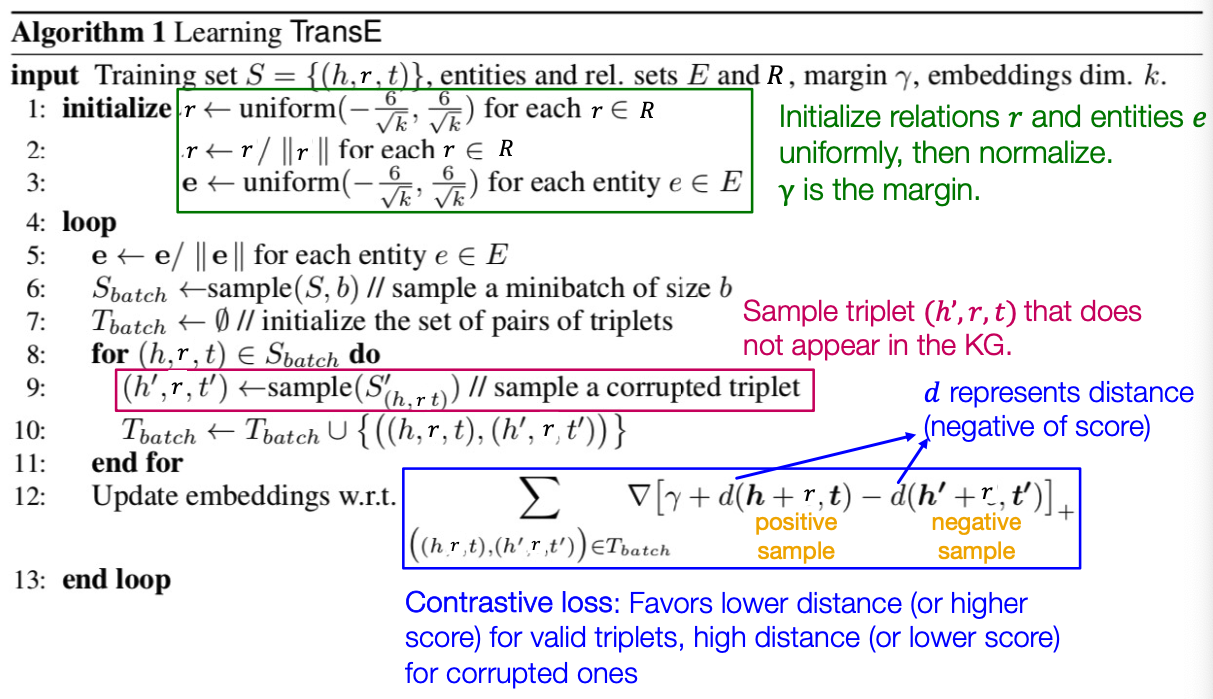
TransE : How to learn?
Relations in a heterogeneous KG have different properties:
Example:Symmetry: If the edge ( h , " R o o m m a t e " , t ) (h,"Roommate",t) ( h , " R oo mma t e " , t ) ( t , " R o m m a t e " , h ) (t,"Rommate",h) ( t , " R o mma t e " , h ) Inverse relation: If the edge ( h , " A d v i s o r " , t ) (h,"Advisor",t) ( h , " A d v i sor " , t ) ( t , " A d v i s e e " , h ) (t,"Advisee",h) ( t , " A d v i see " , h )
Four Relation Patterns
Symmetric (Antisymmetric) Relation: Example:Symmetric: Family, Roommate Antisymmetric: Hypernym (a word with a broader meaning: poodle vs. dog) r ( h , t ) ⟹ r ( t , h ) ( r ( h , t ) ⟹ ¬ r ( t , h ) ) ∀ h , t r(h,t) \Longrightarrow r(t,h) \ (r(h,t)\Longrightarrow \neg r(t,h)) \ \forall h,t r ( h , t ) ⟹ r ( t , h ) ( r ( h , t ) ⟹ ¬ r ( t , h )) ∀ h , t Inverse Relation: Example: (Advisor, Advisee) r 2 ( h , t ) ⟹ r 1 ( t , h ) r_2(h,t) \Longrightarrow r_1(t,h) r 2 ( h , t ) ⟹ r 1 ( t , h ) Composition (Transitive) Relation: Example: My mother’s husband is my father r 1 ( x , y ) ∧ r 2 ( y , z ) ⟹ r 3 ( x , z ) ∀ x , y , z r_1(x,y) \land r_2(y,z) \Longrightarrow r_3(x,z) \ \forall x,y,z r 1 ( x , y ) ∧ r 2 ( y , z ) ⟹ r 3 ( x , z ) ∀ x , y , z 1-to-N relations: Example: r r r r ( h , t 1 ) , r ( h , t 2 ) , ⋯ , r ( h , t n ) r(h,t_1),r(h,t_2),\cdots,r(h,t_n) r ( h , t 1 ) , r ( h , t 2 ) , ⋯ , r ( h , t n ) are all True.
Antisymmetric Relations in TransE
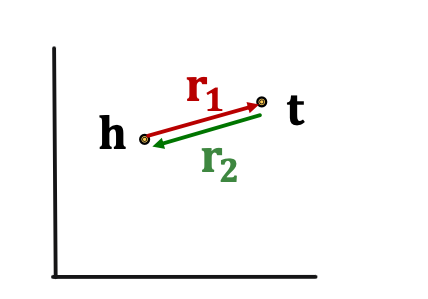
Antisymmetric Relations: Example: Hypernym (a word with a broader meaning: poodle vs. dog) r ( h , t ) ⟹ ¬ r ( t , h ) ∀ h , t r(h,t) \Longrightarrow \neg r(t,h) \ \forall h,t r ( h , t ) ⟹ ¬ r ( t , h ) ∀ h , t TransE can model antisymmetric relations.h + r = t \textbf{h}+ \textbf{r} = \textbf{t} h + r = t t + r ≠ h \textbf{t} + \textbf{r} \neq \textbf{h} t + r = h
Inverse Relations in TransE
Inverse Relation: Example: (Advisor, Advisee) r 2 ( h , t ) ⟹ r 1 ( t , h ) r_2(h,t) \Longrightarrow r_1(t,h) r 2 ( h , t ) ⟹ r 1 ( t , h ) TransE can model inverse relations.h + r 2 = t \textbf{h} + \textbf{r}_2 = \textbf{t} h + r 2 = t r 1 = − r 2 \textbf{r}_1 = - \textbf{r}_2 r 1 = − r 2
Composition in TransE
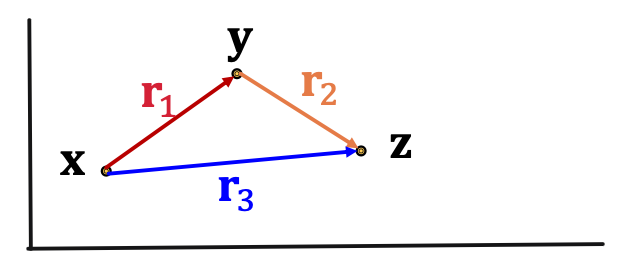
Composition (Transitive) Relation: Example: My mother’s husband is my father. r 1 ( x , y ) ∧ r 2 ( y , z ) ⟹ r 3 ( x , z ) ∀ x , y , z r_1(x,y) \land r_2(y,z) \Longrightarrow r_3(x,z) \ \forall x,y,z r 1 ( x , y ) ∧ r 2 ( y , z ) ⟹ r 3 ( x , z ) ∀ x , y , z TransE can mode composition relation. r 3 = r 1 + r 2 \textbf{r}_3 = \textbf{r}_1 + \textbf{r}_2 r 3 = r 1 + r 2
Symmetric Relation: Limitation
Symmetric Relation: Example: Family, Roommate r ( h , t ) ⟹ r ( t , h ) ∀ h , t r(h,t) \Longrightarrow r(t,h) \ \forall h,t r ( h , t ) ⟹ r ( t , h ) ∀ h , t TransE cannot model symmetric relations only if r = 0 , h = t \textbf{r} =0, \textbf{h} =\textbf{t} r = 0 , h = t
1-to-N Relations: Limitation
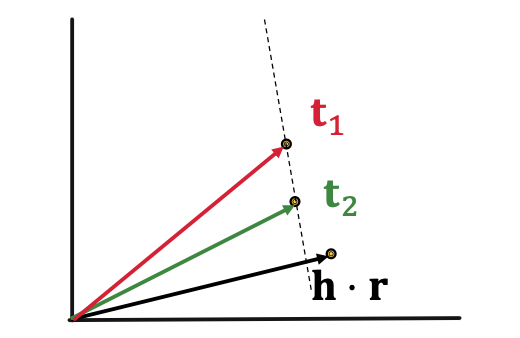
1-to-N Relations: Example: ( h , r , t 1 ) (h,r,t_1) ( h , r , t 1 ) ( h , r , t 2 ) (h,r,t_2) ( h , r , t 2 ) r r r TransE cannot model 1-to-N relationst 1 \textbf{t}_1 t 1 t 2 \textbf{t}_2 t 2 t 1 = h + r = t 2 \textbf{t}_1 = \textbf{h} + \textbf{r} = \textbf{t}_2 t 1 = h + r = t 2 t 1 ≠ t 2 \textbf{t}_1 \neq \textbf{t}_2 t 1 = t 2
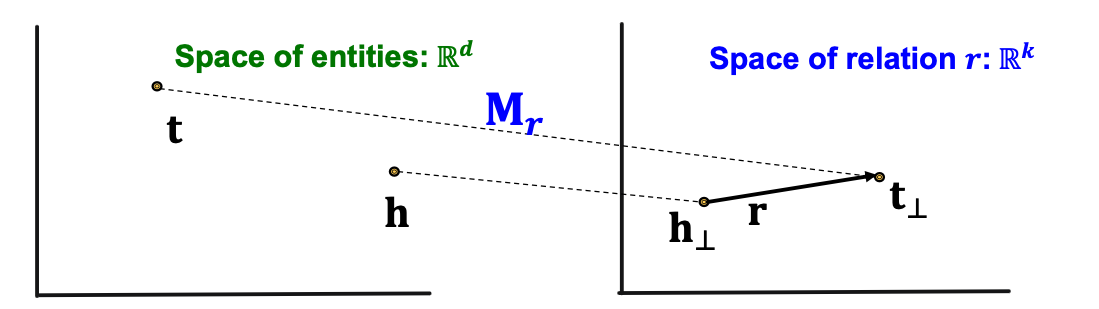
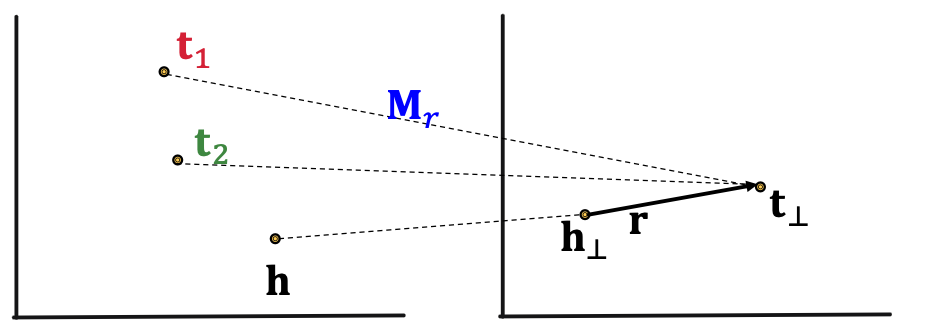
Knowledge Graph Completion: TransR TransE models translation of any relation in the same embedding space. TransR: model entities as vectors in the entity space R d \mathbb{R}^d R d r ∈ R k \textbf{r} \in \mathbb{R}^k r ∈ R k M r ∈ R k × d \textbf{M}_r \in \mathbb{R}^{k \times d} M r ∈ R k × d
TransR
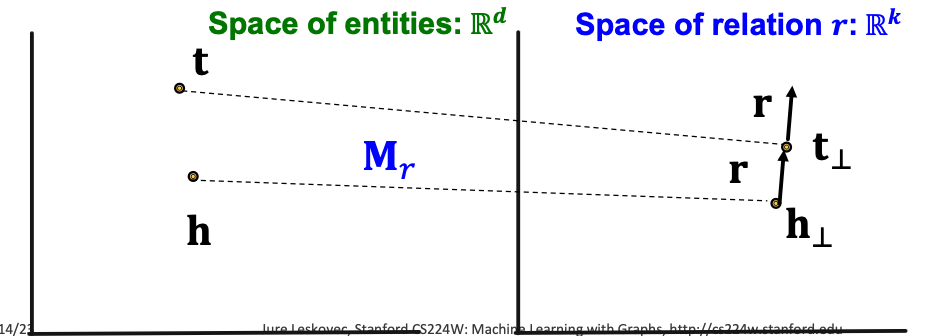
h ⊥ = M r h , t ⊥ = M r t \textbf{h}_{\perp} = \textbf{M}_r \textbf{h} , \ \textbf{t}_{\perp} = \textbf{M}_r \textbf{t} h ⊥ = M r h , t ⊥ = M r t Score function: f r ( h , t ) = − ∣ ∣ h ⊥ + r − t ⊥ ∣ ∣ f_r(h,t) = - ||\textbf{h}_{\perp} + \textbf{r} - \textbf{t}_{\perp}|| f r ( h , t ) = − ∣∣ h ⊥ + r − t ⊥ ∣∣
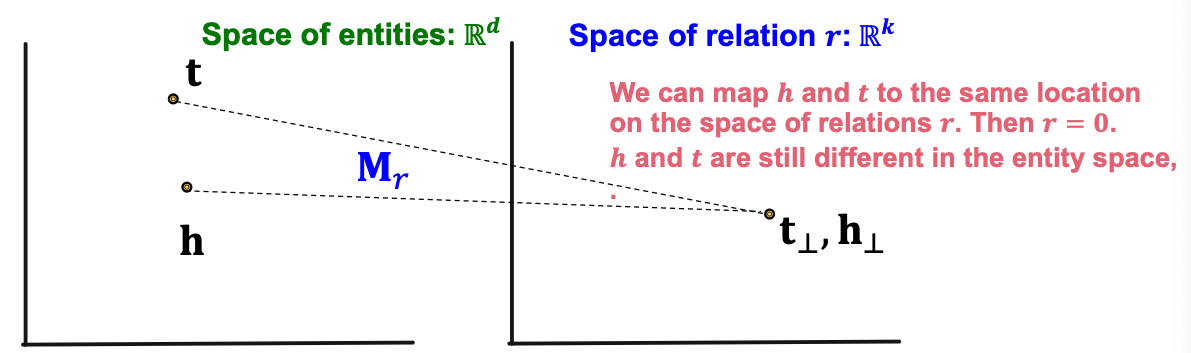
Symmetric Relations in TransR
TransR can model symmetric relations r = 0 , h ⊥ = M r h = M r t = t ⊥ \textbf{r} =0, \textbf{h}_{\perp} = \textbf{M}_r\textbf{h} = \textbf{M}_r \textbf{t} = \textbf{t}_{\perp} r = 0 , h ⊥ = M r h = M r t = t ⊥ Antisymmetric Relations in TransR
TransR can model antisymmetric relations: r ≠ 0 , M r h + r = M r t , ⟹ M r t + r ≠ M r h \begin{align*}
\textbf{r}\neq 0 , \textbf{M}_r\textbf{h} + \textbf{r} &= \textbf{M}_r\textbf{t}, \\
\Longrightarrow \textbf{M}_r\textbf{t} + \textbf{r} &\neq \textbf{M}_r \textbf{h}
\end{align*} r = 0 , M r h + r ⟹ M r t + r = M r t , = M r h
1-to-N Relations in TransR
TransR can model 1-to-N relationsWe can learn M r \textbf{M}_r M r t ⊥ = M r t 1 = M r t 2 \textbf{t}_{\perp} = \textbf{M}_r \textbf{t}_1 = \textbf{M}_r \textbf{t}_2 t ⊥ = M r t 1 = M r t 2 Note that t 1 \textbf{t}_1 t 1 t 2 \textbf{t}_2 t 2
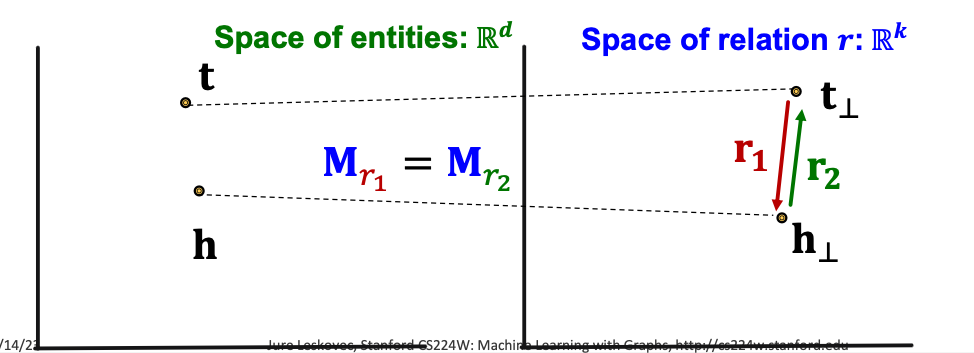
Inverse Relations in TransR
TransR can model inverse relations r 2 = − r 1 , M r 1 = M r 2 \textbf{r}_2 = - \textbf{r}_1, \textbf{M}_{r_1} = \textbf{M}_{r_2} r 2 = − r 1 , M r 1 = M r 2 then
M r 1 t + r 1 = M r 1 h \textbf{M}_{r_1} \textbf{t} + \textbf{r}_1 = \textbf{M}_{r_1} \textbf{h} M r 1 t + r 1 = M r 1 h and
M r 2 h + r 2 = M r 2 t \textbf{M}_{r_2} \textbf{h} + \textbf{r}_2 = \textbf{M}_{r_2}\textbf{t} M r 2 h + r 2 = M r 2 t Composition Relations in TransR
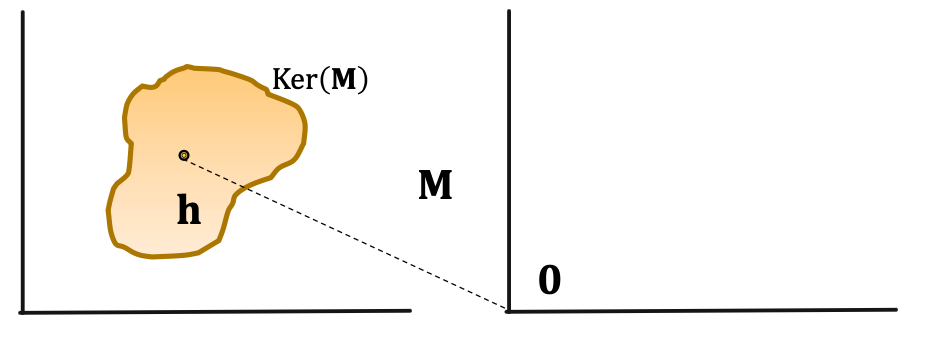
TransR can model composition relations. TransR models a triple with linear functions. Linear functions are chainable!If f ( x ) f(x) f ( x ) g ( x ) g(x) g ( x ) f ( g ( x ) ) f(g(x)) f ( g ( x )) Let: f ( x ) = a ⋅ x + b , g ( x ) = c ⋅ x + d : f(x) =a\cdot x+b, g(x) =c \cdot x + d: f ( x ) = a ⋅ x + b , g ( x ) = c ⋅ x + d : f ( g ( x ) ) = a ( c ⋅ x + d ) + b f(g(x)) = a(c \cdot x+d)+b f ( g ( x )) = a ( c ⋅ x + d ) + b Background:Def: Kernel space of a matrix M M M h ∈ K e r ( M ) , then M ⋅ h = 0 h \in Ker(M), \text{then}\ M \cdot h =0 h ∈ Ker ( M ) , then M ⋅ h = 0 Assume M r 1 g 1 = r 1 M_{r_1}g_1 = r_1 M r 1 g 1 = r 1 M r 2 g 2 = r 2 M_{r_2}g_2 =r_2 M r 2 g 2 = r 2 For r 1 ( x , y ) : r_1(x,y): r 1 ( x , y ) : r 1 ( x , y ) exists ⟹ M r 1 x + r 1 = M r 1 y ⟹ M r 1 ( y − x ) = r 1 , y − x ∈ g 1 + K e r ( M r 1 ) ⟹ y ∈ x + g 1 + K e r ( M r 1 ) r_1(x,y) \ \text{exists} \Longrightarrow M_{r_1}x + r_1 = M_{r_1}y \\
\Longrightarrow M_{r_1}(y-x) = r_1, \ y-x \in g_1 + Ker(M_{r_1})
\\
\Longrightarrow y \in x+ g_1 + Ker(M_{r_1}) r 1 ( x , y ) exists ⟹ M r 1 x + r 1 = M r 1 y ⟹ M r 1 ( y − x ) = r 1 , y − x ∈ g 1 + Ker ( M r 1 ) ⟹ y ∈ x + g 1 + Ker ( M r 1 ) Same for r 2 ( y , z ) r_2(y,z) r 2 ( y , z ) r 2 ( y , z ) exists ⟹ M r 2 y + r 2 = M r 2 z ⟹ z − y ∈ g 2 + K e r ( M r 2 ) ⟹ z ∈ y + g 2 + K e r ( M r 2 ) r_2(y,z) \ \text{exists} \Longrightarrow M_{r_2}y+r_2 = M_{r_2}z \\
\Longrightarrow z-y \in g_2 + Ker(M_{r_2}) \Longrightarrow z \in y+g_2 + Ker(M_{r_2}) r 2 ( y , z ) exists ⟹ M r 2 y + r 2 = M r 2 z ⟹ z − y ∈ g 2 + Ker ( M r 2 ) ⟹ z ∈ y + g 2 + Ker ( M r 2 ) z ∈ x + g 1 + g 2 + K e r ( M r 1 ) + K e r ( M r 2 ) z \in x+g_1+g_2+Ker(M_{r_1}) + Ker(M_{r_2}) z ∈ x + g 1 + g 2 + Ker ( M r 1 ) + Ker ( M r 2 ) Construct M r 3 , M_{r_3}, M r 3 , K e r ( M r 3 ) = K e r ( M r 1 ) + K e r ( M r 2 ) Ker(M_{r_3}) = Ker(M_{r_1})+ Ker(M_{r_2}) Ker ( M r 3 ) = Ker ( M r 1 ) + Ker ( M r 2 ) Set r 3 = M r 3 ( g 1 + g 2 ) r_3 = M_{r_3} (g_1+g_2) r 3 = M r 3 ( g 1 + g 2 ) We have M r 3 x + r 3 = M r 3 z M_{r_3} x + r_3 = M_{r_3}z M r 3 x + r 3 = M r 3 z
Knowledge Graph Completion: DistMult New Idea: Bilinear Modeling
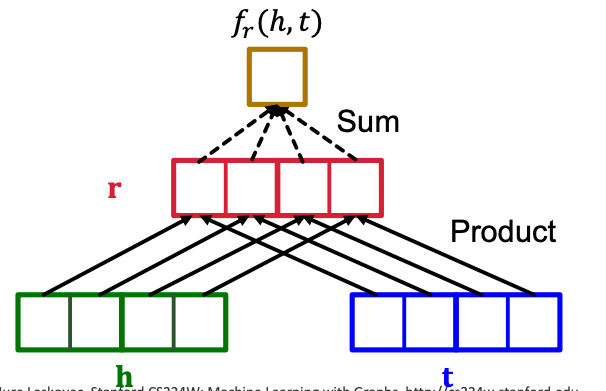
So far: The scoring function f r ( h , t ) f_r(h,t) f r ( h , t ) L 1 / L 2 L_1/L_2 L 1 / L 2 Idea: Use bilinear modeling: Score function f r ( h , t ) = h ⋅ A ⋅ t h , t ∈ R k , A ∈ R k × k f_r(h,t) = h \cdot A \cdot t \ \ h,t \in \mathbb{R}^k,A\in \mathbb{R}^{k\times k} f r ( h , t ) = h ⋅ A ⋅ t h , t ∈ R k , A ∈ R k × k Problem: Too general and prone to overfittingMatrix A is too expressive Fix: Limit A to be diagonal
New Idea: Bilinear Modeling
DistMult: Entities & relations are vectors in R k \mathbb{R}^k R k Score function: h , r , t ∈ R k h,r,t \in \mathbb{R}^k h , r , t ∈ R k f r ( h , t ) = < h , r , t > = ∑ i h r ⋅ r i ⋅ t i f_r(h,t) = <h,r,t> = \sum_{i}h_r\cdot r_i \cdot t_i f r ( h , t ) =< h , r , t >= i ∑ h r ⋅ r i ⋅ t i Can be viewed as a cosine similarity between h ⋅ r h\cdot r h ⋅ r t t t h ⋅ r h \cdot r h ⋅ r [ h ⋅ r ] i = h i ⋅ r i [h \cdot r]_i = h_i \cdot r_i [ h ⋅ r ] i = h i ⋅ r i
1-to-N Relations in DistMult
1-to-N Relation:If ( h , r , t 1 ) (h,r,t_1) ( h , r , t 1 ) ( h , r , t 2 ) (h,r,t_2) ( h , r , t 2 ) DistMult can model 1-to-N relations < h , r , t 1 > = < h , r , t 2 > <h,r,t_1> = <h,r,t_2> < h , r , t 1 >=< h , r , t 2 >
Symmetric Relations in DistMult
DistMult can naturally model symmetric relationsDue to the commutative property of multiplication f r ( h , t ) = < h , r , t > = ∑ i h i ⋅ r i ⋅ t i = < t , r , h > = f r ( t , h ) f_r(h,t) = <h,r,t> = \sum_{i} h_i \cdot r_i \cdot t_i = <t,r,h> = f_r(t,h) f r ( h , t ) =< h , r , t >= i ∑ h i ⋅ r i ⋅ t i =< t , r , h >= f r ( t , h ) Limitation: Antisymmetric Relations
DisMult can not model antisymmetric relationsr ( h , t ) r(h,t) r ( h , t ) r ( t , h ) r(t,h) r ( t , h ) f r ( h , t ) = < h , r , t > = < t , r , h > = f r ( t , h ) f_r(h,t) = <h,r,t> = <t,r,h> = f_r(t,h) f r ( h , t ) =< h , r , t >=< t , r , h >= f r ( t , h )
Limitation: Inverse Relations
DistMult can not model inverse relationsAssume DistMult does model inverse relations: f r 2 ( h , t ) = < h , r 2 , t > = < t , r 1 , h > = f r 1 ( t , h ) f_{r_2}(h,t) = <h,r_2,t> = <t,r_1,h> = f_{r_1}(t,h) f r 2 ( h , t ) =< h , r 2 , t >=< t , r 1 , h >= f r 1 ( t , h ) For example, r 2 = r 1 r_2 =r_1 r 2 = r 1 But semantically this does not make sense: The embedding of “Advisor” relation should not be the same as “Advisee” relation.
Limitation: Composition Relations
DistMult can not model composition of relationsBecause dot product is commutative ( a ⋅ b = b ⋅ a ) (a\cdot b = b \cdot a) ( a ⋅ b = b ⋅ a )
Knowledge Graph Completion: ComplEx
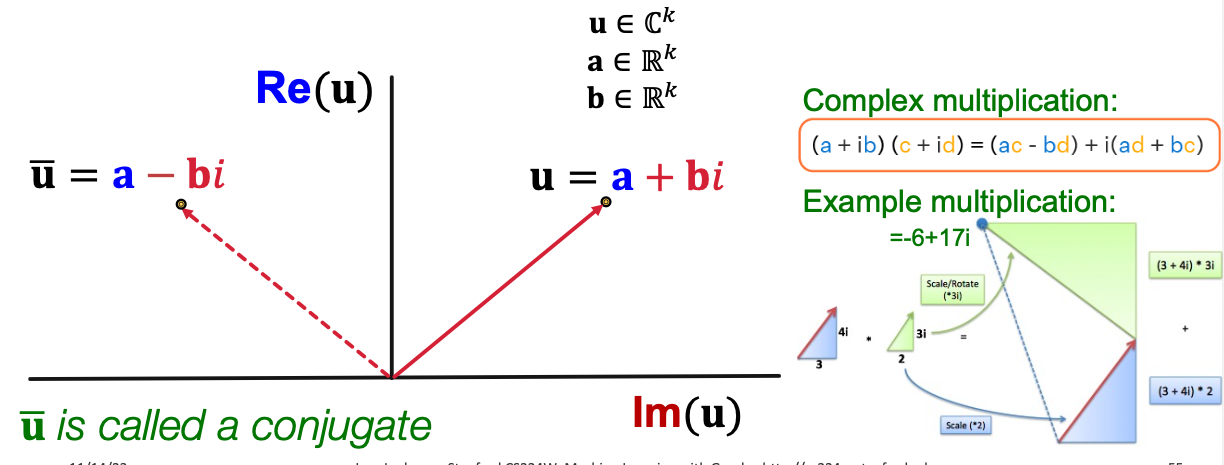
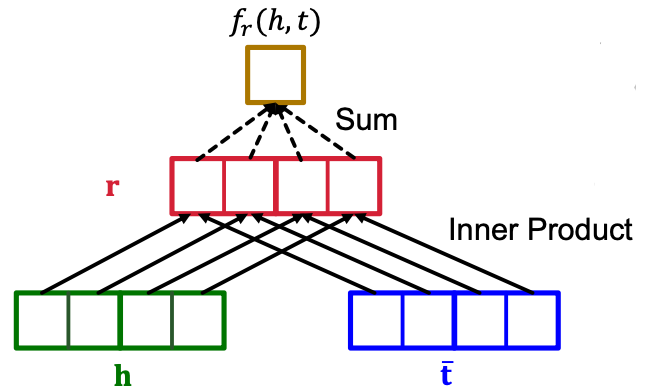
Based on DistMult, ComplEx embeds entities and relations in Complex vector space ComplEx: model entities and relations using vector in C k \mathbb{C}^k C k f r ( h , t ) = R e ( ∑ i h i ⋅ r i ⋅ t ‾ i ) = < R e ( h i ) , R e ( r i ) , R e ( t i ) > + < R e ( h i ) , I m ( r i ) , I m ( t i ) > + < I m ( h i ) , R e ( r i ) , I m ( t i ) > − < I m ( h i ) , I m ( r i ) , R e ( t i ) > \begin{align*}
f_r(h,t) &= Re(\sum_i h_i \cdot r_i \cdot \overline{t}_i) \\
& = <Re(h_i),Re(r_i),Re(t_i)> + <Re(h_i),Im(r_i),Im(t_i)> \\
&+<Im(h_i),Re(r_i),Im(t_i)> - <Im(h_i),Im(r_i),Re(t_i)>
\end{align*} f r ( h , t ) = R e ( i ∑ h i ⋅ r i ⋅ t i ) =< R e ( h i ) , R e ( r i ) , R e ( t i ) > + < R e ( h i ) , I m ( r i ) , I m ( t i ) > + < I m ( h i ) , R e ( r i ) , I m ( t i ) > − < I m ( h i ) , I m ( r i ) , R e ( t i ) >
Antisymmetric Relations in ComplEx
ComplEx can model antisymmetric relations
Symmetric Relations in ComplEx
ComplEx can model symmetric relationsWhen I m ( r ) = 0 Im(r) = 0 I m ( r ) = 0 f r ( h , t ) = R e ( ∑ i h i ⋅ r i ⋅ t ‾ i ) = ∑ i R e ( r i ⋅ h i ⋅ t ‾ i ) = ∑ i r i ⋅ R e ( h i ⋅ t ‾ i ) = ∑ i r i ⋅ R e ( h ‾ i ⋅ t i ) = ∑ i R e ( r i ⋅ h ‾ i ⋅ t i ) = f r ( t , h ) \begin{align*}
f_r(h,t) &= Re(\sum_i h_i \cdot r_i \cdot \overline{t}_i) \\
&= \sum_iRe(r_i \cdot h_i \cdot \overline{t}_i)\\
&=\sum_i r_i \cdot Re(h_i\cdot \overline{t}_i) \\
&= \sum_i r_i \cdot Re(\overline{h}_i\cdot t_i) \\
&= \sum_i Re(r_i \cdot \overline{h}_i \cdot t_i)\\
&= f_r(t,h)
\end{align*} f r ( h , t ) = R e ( i ∑ h i ⋅ r i ⋅ t i ) = i ∑ R e ( r i ⋅ h i ⋅ t i ) = i ∑ r i ⋅ R e ( h i ⋅ t i ) = i ∑ r i ⋅ R e ( h i ⋅ t i ) = i ∑ R e ( r i ⋅ h i ⋅ t i ) = f r ( t , h )
Inverser Relations in ComplEX
ComplEx can model inverse relationsr 1 = r 2 ‾ r_1 = \overline{r_2} r 1 = r 2 ComplEx conjugate ofr 2 = arg max r R e ( < h , r , t ‾ > ) r_2 = \argmax_r Re(<h,r,\overline{t}>) r 2 = arg max r R e ( < h , r , t > ) r 1 = arg max r R e ( < t , r , h ‾ > ) r_1 = \argmax_r Re(<t,r,\overline{h}>) r 1 = arg max r R e ( < t , r , h > )
Composition and 1-to-N in ComplEx
ComplEx share the same property with DistMultCan not model composition relations Can model 1-to-N relations